| tags: [ Data Cleaning Genomic Data Linux PLINK ] categories: [Coding Experiments ]
Generating basic statistics for final genomic data sets
Introduction
After obtaining the unfiltered WGS data and converting the SNP-array data to a hg38 genome reference build, I can generate basic stats, QC, and merge. There should not be anymore changes to the base data sets moving forward.
Methods and Results
1.Find allele frequencies in both file sets
plink1.9 --bfile NI.snp.hg38_final --freq --out plink_output/snp_allele_freqOutput: - 26,055,300 variants loaded - 506 individuals (247 males, 259 females) - 45 founders - genotyping rate is 98.69%
plink1.9 --bfile NI_wgs_merged_snps --freq --out plink_output/wgs_allele_freqOutput: - 19,208,586 variants loaded - 108 individuals (58 males, 50 females) - 108 founders - genotyping rate is 99.68%
2. Plot histogram of allele frequency distributions in both file sets
wgs_allele_freq <- read.table('C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/plink_output/wgs_allele_freq.frq', header = T)
hist(wgs_allele_freq$MAF, main = "Allele Frequency Distributions of WGS Data", xlab = "Minor Allele Frequency", xlim = c(0.0, 0.5), col = "lightpink")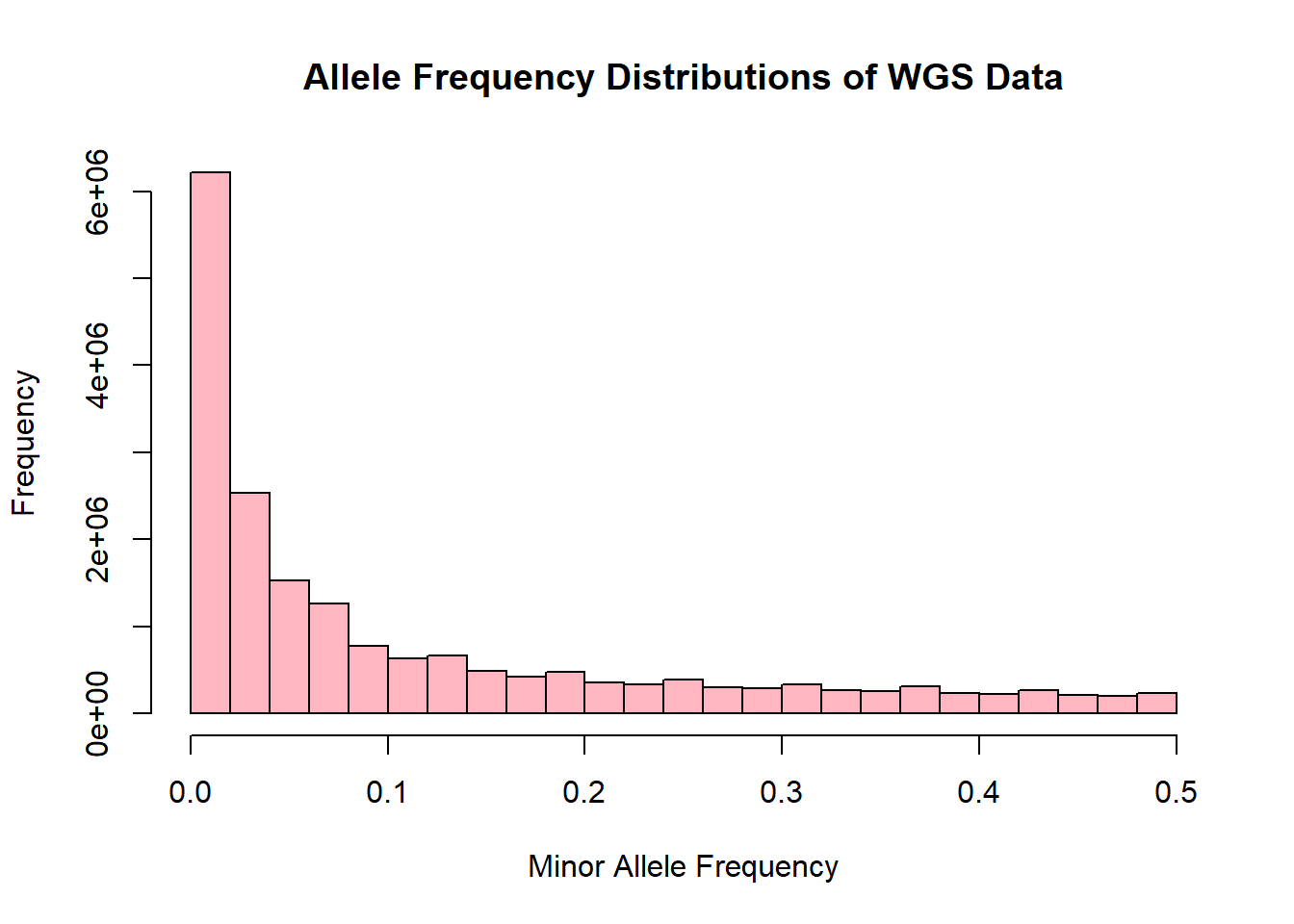
snp_allele_freq <- read.table('C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/plink_output/snp_allele_freq.frq', header = T)
hist(snp_allele_freq$MAF, main = "Allele Frequency Distribution of SNP Data", xlab = "Minor Allele Frequency", xlim = c(0.0, 0.5), col = "cadetblue1")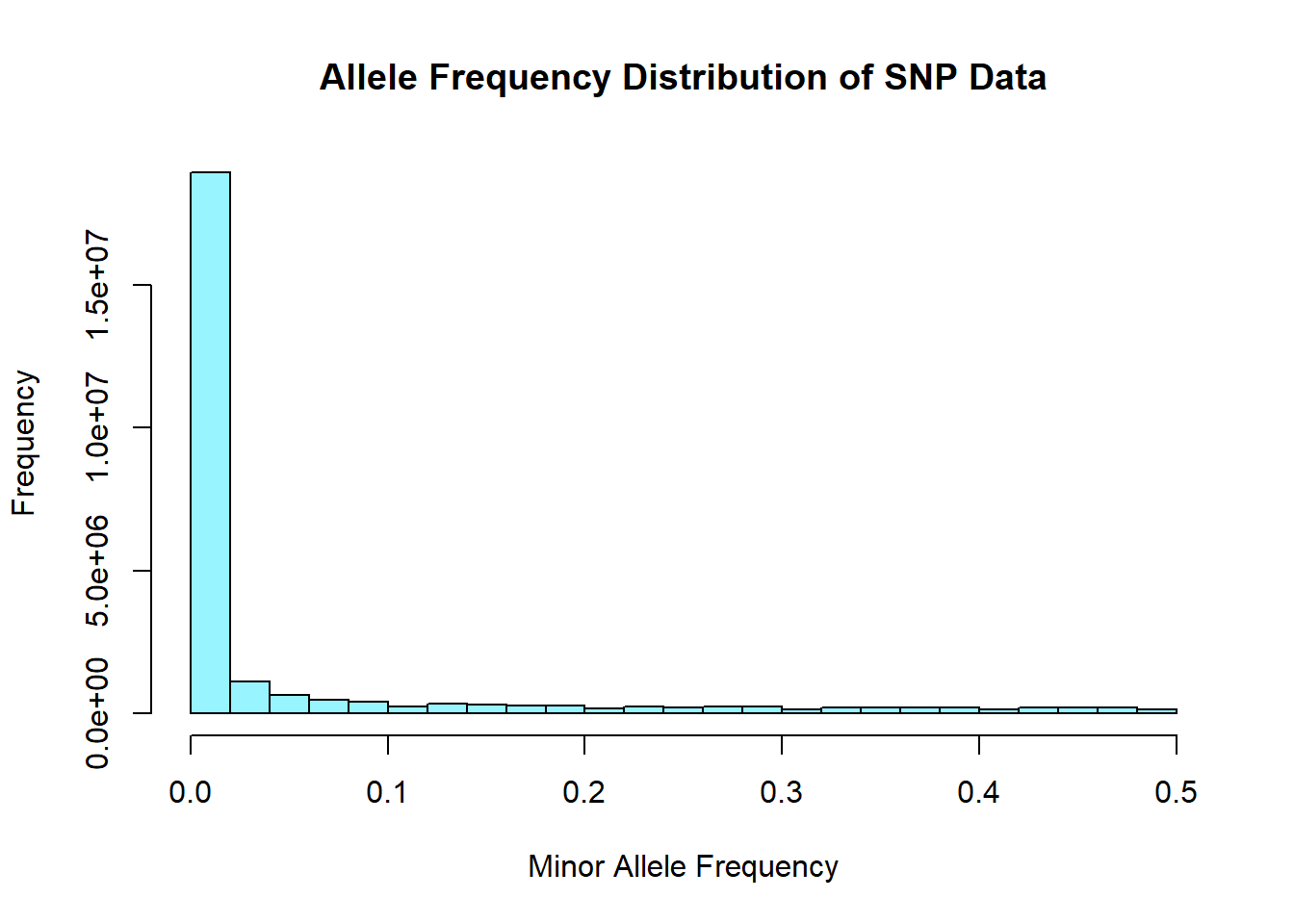
3. Generate missingness statistics
plink1.9 --bfile NI_wgs_merged_snps --missing --out plink_output/wgs_missing
plink1.9 --bfile NI.snps.hg38_final --missing --out plink_output/snp_missingMissingness statistics generate two files: one which details missingess rate for individuals and one for SNPs. For each individual, the file contains family and individual IDs, whether they have missing phenotypes, the number of missing SNPs, number of non-obligatory missing genotypes and the proportion of missing SNPs. For the SNPs, the file contains rsIDs, the chromosome number, the number of individuals missing that SNP, number of non-obligatory missing genotypes, and the proportion of samples missing that SNP.
4. Generate hardy-weinberg test statistics
plink1.9 --bfile NI_wgs_merged_snps --hardy --out plink_output/wgs_hardy
plink1.9 --bfile NI.snps.hg38_final --hardy --out plink_output/snp_hardyThe hardy-weinberg test statistics generates a file set that contains the SNP IDs, a code indicating sample, minor allele code, major allele code, genotype counts, observed heterozygosity, expected heterozygosity, and a HWE p-value.
5. Filter out variants based on HWE p-value
plink1.9 --bfile NI_wgs_merged_snps --hwe 1.8e-7 --make-bed --out plink_output/wgs_hwe_filter
plink1.9 --bfile NI.snp.hg38_final --hwe 1.8e-7 --make-bed --out plink_output/snp_hwe_filterNote: this step creates a new set of files
Output (WGS): - 305,519 variants were filtered out - 19,903,067 variants remain
Output (SNP): - 17 variants were filtered out - 26,055,283 variants remain
Number of SNPs filtered out seem incredibly small?
6. Perform trial merge to generate file with variants with 3+ alleles
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/wgs_hwe_filter --bmerge plink_output/snp_hwe_filter.bed plink_output/snp_hwe_filter.bim plink_output/snp_hwe_filter.fam --make-bed --out plink_output/trial_mergeNote: despite the reference genome build conversion on the SNP-array data, this trial merge still resulted in a large number of multiple position warnings (600+). These will be excluded from the data sets, along with the variants that appear to have 3+ alleles (10,344 variants).
7. Exclude variants with 3+ alleles from both files
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/wgs_hwe_filter --exclude plink_output/trial_merge-merge.missnp --make-bed --out plink_output/wgs_multall_exclude
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/snp_hwe_filter --exclude plink_output/trial_merge-merge.missnp --make-bed --out plink_output/snp_multall_excludeWGS: 18,892,723 variants remain SNP: 26,044,939 variants remain
Note: this step creates new file sets.
8. Exclude variants with multiple position warnings
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/wgs_multall_exclude --exclude plink_output/multpos_var.txt --make-bed --out plink_output/wgs_multpos_outOutput: - 18,892,340 variants remain (383 variants removed)
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/snp_multall_exclude --exclude plink_output/multpos_var.txt --make-bed --out plink_output/snp_multpos_outOutput: - 26,044,556 variants remain (383 variants removed)
Why is this process only removing 383 variants when there are 691 variants with multiple position warnings?
9. Re-try merge after exclusion of multi-allelic variants and variants with multiple position warnings.
plink1.9 --bfile plink_output/wgs_multpos_out --bmerge plink_output/snp_multpos_out.bed plink_output/snp_multpos_out.bim plink_output/snp_multpos_out.fam --make-bed --out plink_output/multiple_out_mergeNote: had to transfer to taurus for this step. I transferred only the wgs/snp_multpos_out file sets.
- 18,892,340 variants loaded from WGS files
- 26,044,556 variants loaded from SNP files
- 9,143,298 variants are common across both file sets
- 154,268 variants with same-position warnings
- merged files contain 35,793,598 variants
- genotyping rate is 68.45%
The merge function in PLINK appears to exclude variants that are common across both file sets. Will have to manually extract common variants in R by comparing both data sets.