| tags: [ Gaston GCTA Genomic Data GWAS Heritability ] categories: [Coding Experiments ]
Performing GWAS on heritable traits
require(magrittr)## Loading required package: magrittrrequire(dplyr)## Loading required package: dplyr##
## Attaching package: 'dplyr'## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## filter, lag## The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
##
## intersect, setdiff, setequal, unionrequire(gaston)## Loading required package: gaston## Loading required package: Rcpp## Loading required package: RcppParallel##
## Attaching package: 'RcppParallel'## The following object is masked from 'package:Rcpp':
##
## LdFlags## Gaston set number of threads to 2. Use setThreadOptions() to modify this.##
## Attaching package: 'gaston'## The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
##
## sigma## The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
##
## cbind, rbindrequire(qqman)## Loading required package: qqman## ## For example usage please run: vignette('qqman')## ## Citation appreciated but not required:## Turner, S.D. qqman: an R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. biorXiv DOI: 10.1101/005165 (2014).## ##
## Attaching package: 'qqman'## The following object is masked from 'package:gaston':
##
## manhattanIntroduction
After running GWAS parallel in GCTA and gaston, we were concerned that GCTA was over burdening the test because the program was developed to deal with very large amounts of data. Considering our sample size was very small, random effects that may be in the GCTA models could have very significant effects on the GWAS results. This was evident on the manhattan plots generated for the same data, with the same adjustments between GCTA and gaston. In light of this, we have decided to move the GWAS analysis back to gaston.
I will be performing GWAS on 21 heritable traits (16 individual phenotypes and 5 principal components). I will be using the likelihood ratio test (LRT) as opposed to the wald test and score test as it is the most commonly used in GWAS and is suitable for smaller sample sizes (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4547377/). I will also be correcting for any effects of population stratification by including two prinicipal components as I have done with the heritability estimates.
For the Norfolk Island population, we set a genome-wide signficance threshold of p < 1.84e-7 rather than the general p < 5e-8 because that was calculated specifically for the sample size in the study.
Methods and Results
1. Load phenotypic data
nies_pheno_020918 <- read.csv('C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/nies_pheno_020918.csv', header = T)
head(nies_pheno_020918)## Fam.ID UUID R.Logmar.VA L.Logmar.VA R.Sph..pre.dilate.
## 1 1 219960 0.02 -0.04 0.25
## 2 1 313180 0.10 0.16 0.00
## 3 1 320511 -0.06 0.02 1.00
## 4 1 400011 -0.14 -0.10 0.75
## 5 1 400013 0.30 0.30 1.50
## 6 1 316131 0.08 0.26 2.00
## R.Cyl..pre.dilate. R.Axis..pre.dilate. L.Sph..pre.dilate.
## 1 0.00 0 0.25
## 2 -0.75 28 -0.50
## 3 0.00 0 1.25
## 4 -0.25 157 1.25
## 5 -0.25 82 1.75
## 6 -1.00 69 1.00
## L.Cyl..pre.dilate. L.Axis..pre.dilate. R.K.value.H R.K.Value.H.Axis
## 1 -0.50 79 42.00 2
## 2 -0.25 164 41.25 7
## 3 -0.25 29 42.50 177
## 4 -0.50 20 42.50 165
## 5 -0.50 100 43.00 0
## 6 -1.00 114 42.75 63
## R.K.value.V R.K.value.V.Axis L.K.value.H L.K.value.H.Axis L.K.value.V
## 1 43.00 92 42.50 5 43.50
## 2 42.25 97 41.50 168 42.00
## 3 43.50 87 42.00 170 42.50
## 4 43.25 75 42.75 17 43.25
## 5 43.00 90 42.75 111 43.00
## 6 44.00 153 43.00 115 43.50
## L.K.value.V.Axis R.Pachimetry L.Pachimetry R.Axial.Length L.Axial.Length
## 1 95 532 554 24.31 24.10
## 2 78 608 612 25.02 25.21
## 3 80 499 512 23.37 23.65
## 4 107 602 601 23.32 23.34
## 5 21 552 550 22.93 22.70
## 6 25 583 588 23.49 23.54
## R.AC.Depth L.AC.Depth R.IOP.mmHg L.IOP.mmHg R.CDR L.CDR totaluvafmm
## 1 3.09 3.03 14 14 0.9 0.9 0.0
## 2 3.38 3.92 16 15 0.9 0.7 74.4
## 3 3.29 3.08 17 18 0.4 0.4 27.5
## 4 3.81 3.83 15 17 0.6 0.6 47.0
## 5 3.22 3.13 18 18 0.4 0.4 20.1
## 6 3.24 3.04 12 12 0.3 0.3 12.92. Load genomic data (bed/bim/fam)
merged_nies_210818 <- read.bed.matrix("C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/merged_nies/merged_nies_geno_210818.bed")## Reading C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/merged_nies/merged_nies_geno_210818.fam
## Reading C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/merged_nies/merged_nies_geno_210818.bim
## Reading C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/merged_nies/merged_nies_geno_210818.bed
## ped stats and snps stats have been set.
## 'p' has been set.
## 'mu' and 'sigma' have been set.3. Generate GRM, eigenK, and principal components
merged_nies_GRM <- GRM(merged_nies_210818)
merged_nies_eiK <- eigen(merged_nies_GRM)
merged_nies_eiK$values[ merged_nies_eiK$values < 0] <- 0
merged_nies_PC <- sweep(merged_nies_eiK$vectors, 2, sqrt(merged_nies_eiK$values), "*")The genetic relationship matrix (GRM) will be used to account for the degree of relatedness among individuals, and the principal components will be used to correct for hiden population structure. Both of these ensure that any associations detected are not due to relatedness or hidden structures in the data i.e. they are true phenotypic-variant associations.
4. Perform GWAS on R K-value V (most heritable trait)
r_kvalV_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_pheno_020918$R.K.value.V, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
r_kvalV_gwas <- na.omit(r_kvalV_gwas)
r_kvalV_gwas_filtered <- r_kvalV_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
qqman::manhattan(x = r_kvalV_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "R K-value V", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)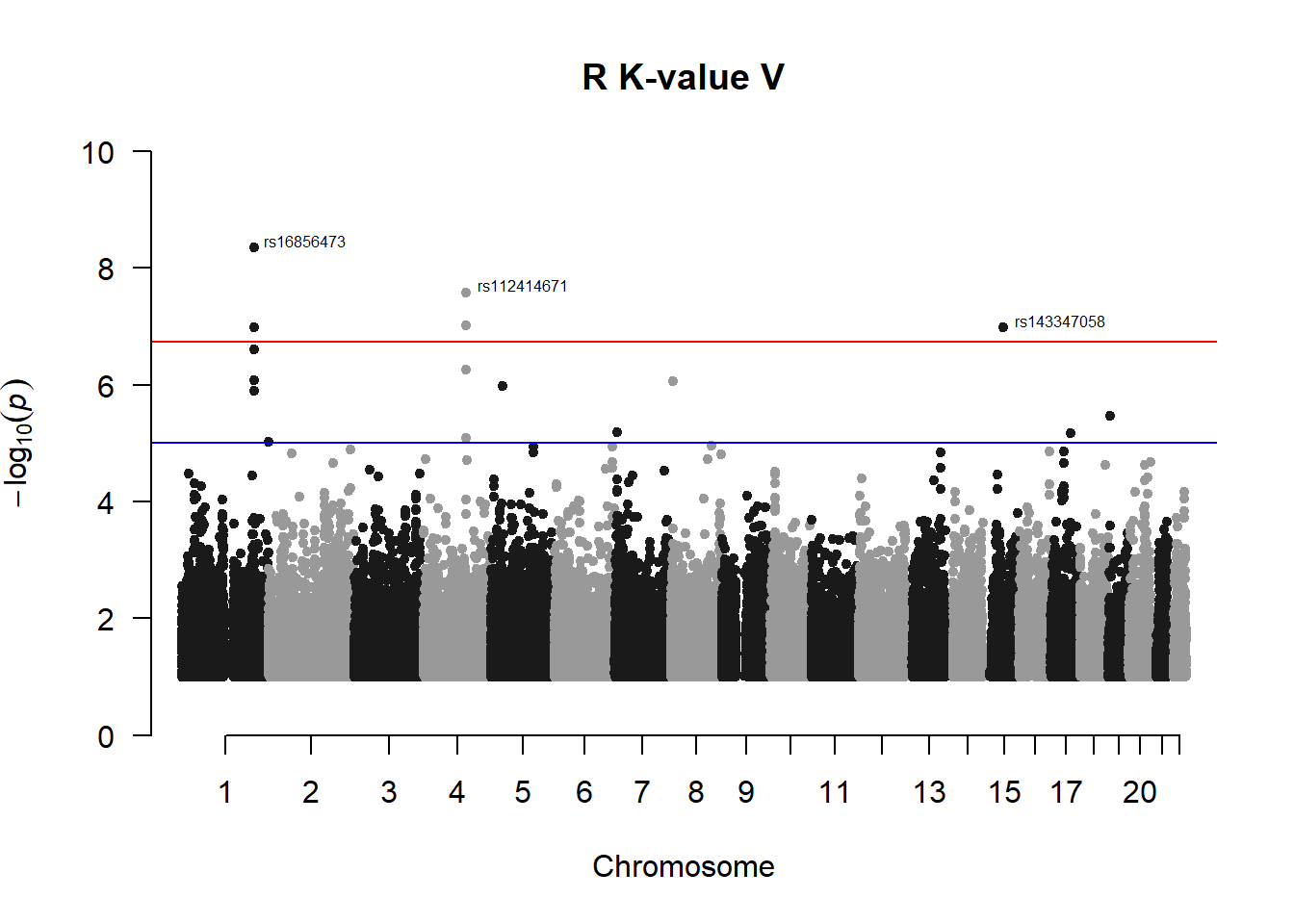
5. Repeat GWAS on other heritable traits
nies_heritable_pheno <- read.csv('C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/nies_heritable_pheno.csv', header = T)
head(nies_heritable_pheno)## UUID R.K.value.V L.Pachimetry coord.Dim.1 R.Pachimetry R.CDR
## 1 219960 43.00 554 -1.3318012 532 0.9
## 2 313180 42.25 612 -3.7993478 608 0.9
## 3 320511 43.50 512 -0.4961408 499 0.4
## 4 400011 43.25 601 -0.7904275 602 0.6
## 5 400013 43.00 550 0.4462229 552 0.4
## 6 316131 44.00 588 0.2319576 583 0.3
## L.K.value.V R.Cyl..pre.dilate. L.CDR R.K.value.H coord.Dim.4 totaluvafmm
## 1 43.50 0.00 0.9 42.00 0.8399155 0.0
## 2 42.00 -0.75 0.7 41.25 2.0776045 74.4
## 3 42.50 0.00 0.4 42.50 -0.9796890 27.5
## 4 43.25 -0.25 0.6 42.50 1.5424175 47.0
## 5 43.00 -0.25 0.4 43.00 0.4965415 20.1
## 6 43.50 -1.00 0.3 42.75 -0.4216580 12.9
## R.Axial.Length L.Axial.Length R.AC.Depth L.K.value.H L.AC.Depth
## 1 24.31 24.10 3.09 42.50 3.03
## 2 25.02 25.21 3.38 41.50 3.92
## 3 23.37 23.65 3.29 42.00 3.08
## 4 23.32 23.34 3.81 42.75 3.83
## 5 22.93 22.70 3.22 42.75 3.13
## 6 23.49 23.54 3.24 43.00 3.04
## coord.Dim.7 R.IOP.mmHg coord.Dim.3 coord.Dim.8 L.IOP.mmHg
## 1 2.8552892 14 0.75849347 -1.0126837 14
## 2 2.2543673 16 0.41111735 0.3400838 15
## 3 -1.1828388 17 -0.62633667 0.1104747 18
## 4 2.2077992 15 -1.18429936 1.5903830 17
## 5 -0.5839491 18 -0.03864912 -0.2245313 18
## 6 1.1946733 12 0.16696557 -0.8347539 12I compiled the data for the heritable traits into a new spreadsheet (loaded above).
pheno_gwas <- NULL
for (i in c(2:ncol(nies_heritable_pheno))){
pheno_colnames <- colnames(nies_heritable_pheno[i])
her_pheno_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno[,i], method = "lmm",
test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p =2)
her_pheno_gwas <- na.omit(her_pheno_gwas)
pheno_gwas_filtered <- her_pheno_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
qqman::manhattan(x = pheno_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = paste(pheno_colnames))
pheno_gwas <- pheno_gwas_filtered
}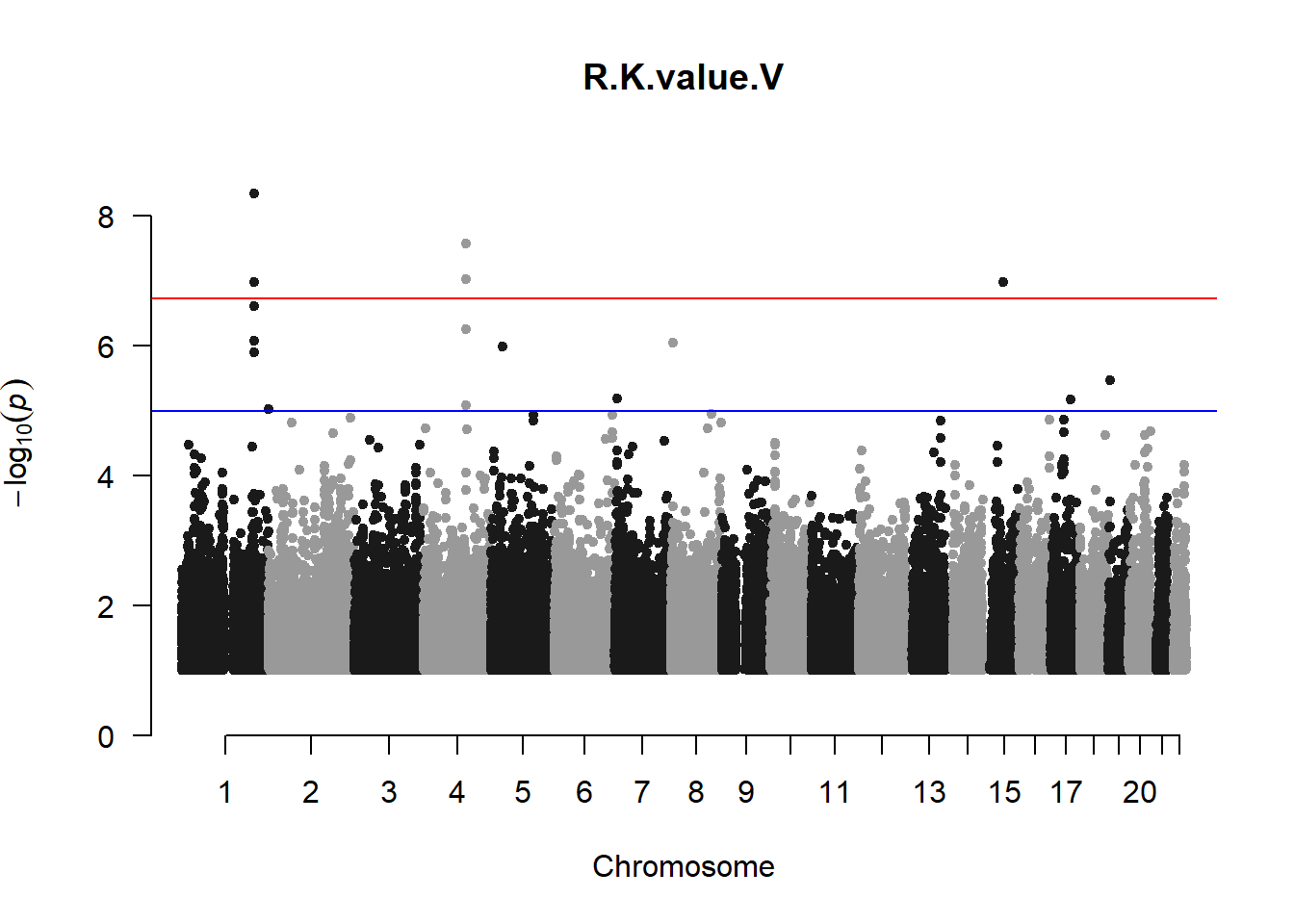
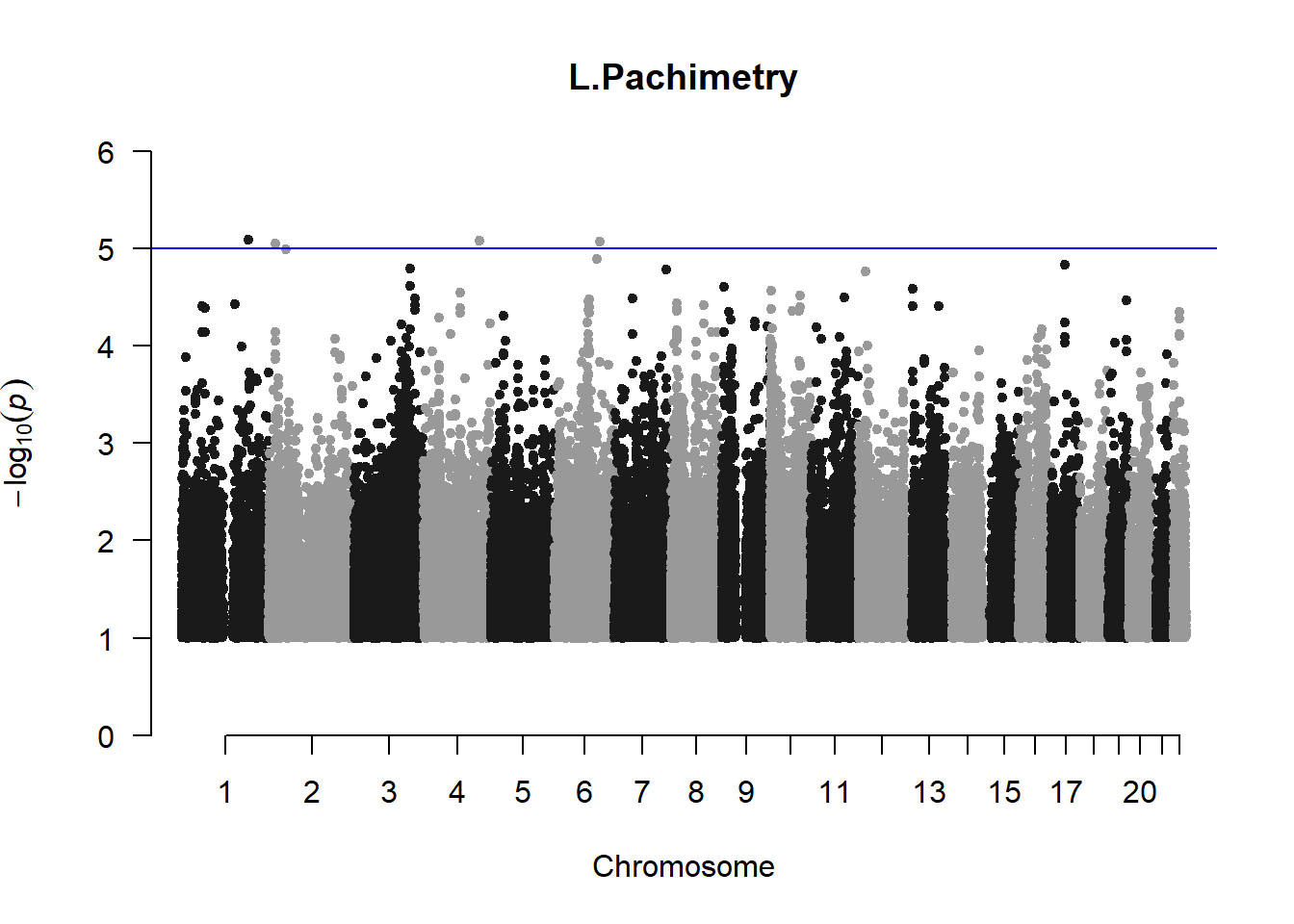
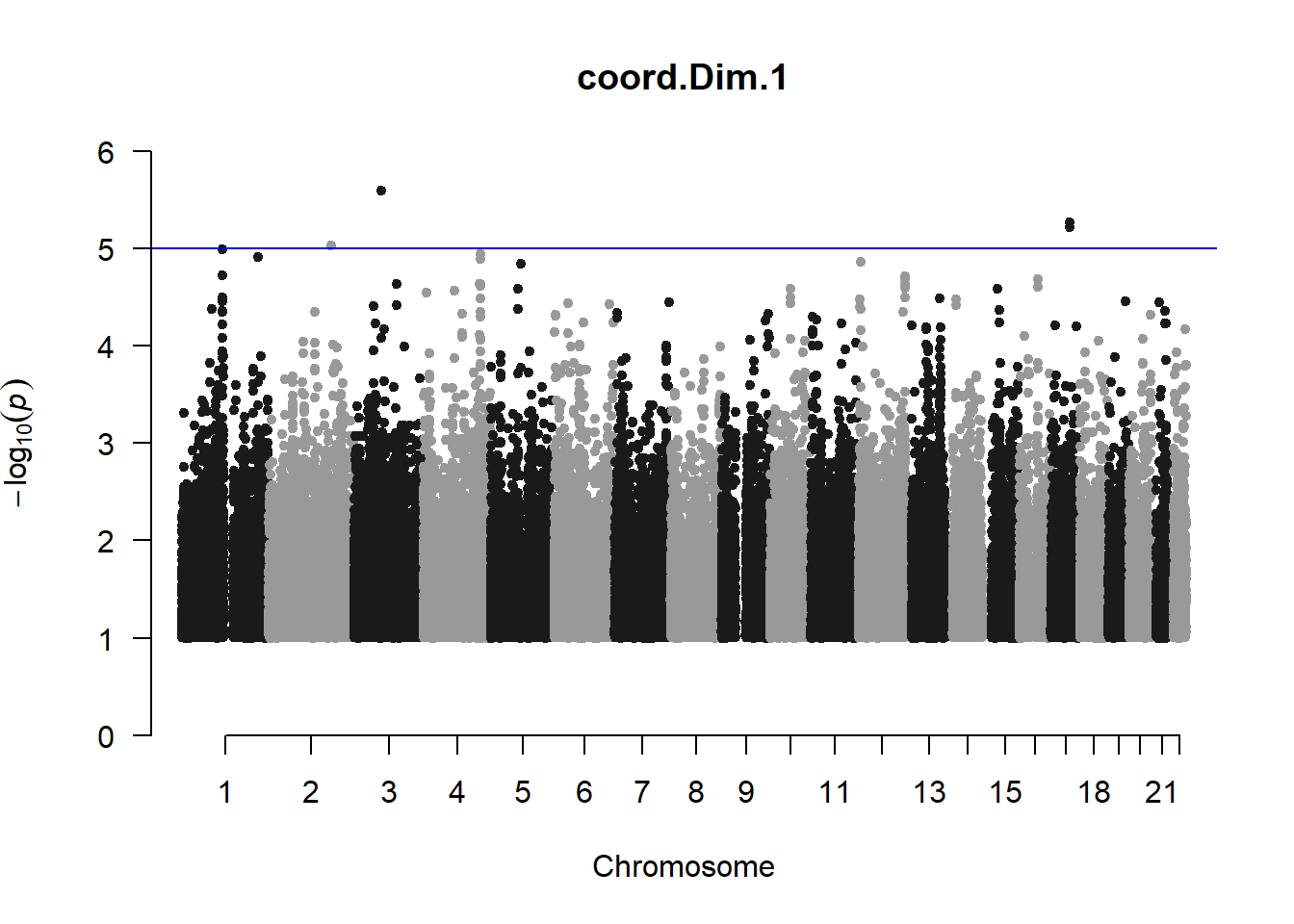
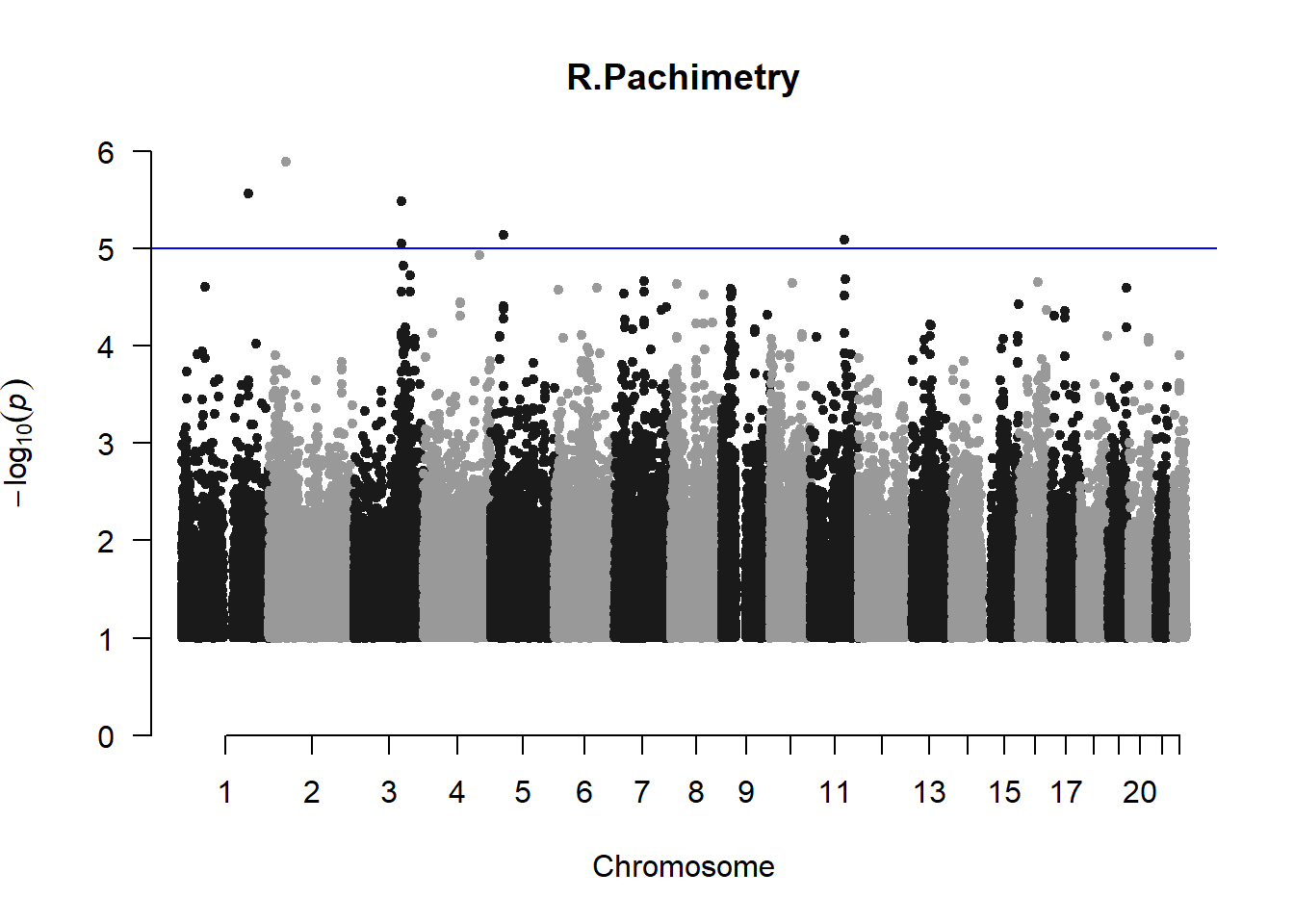
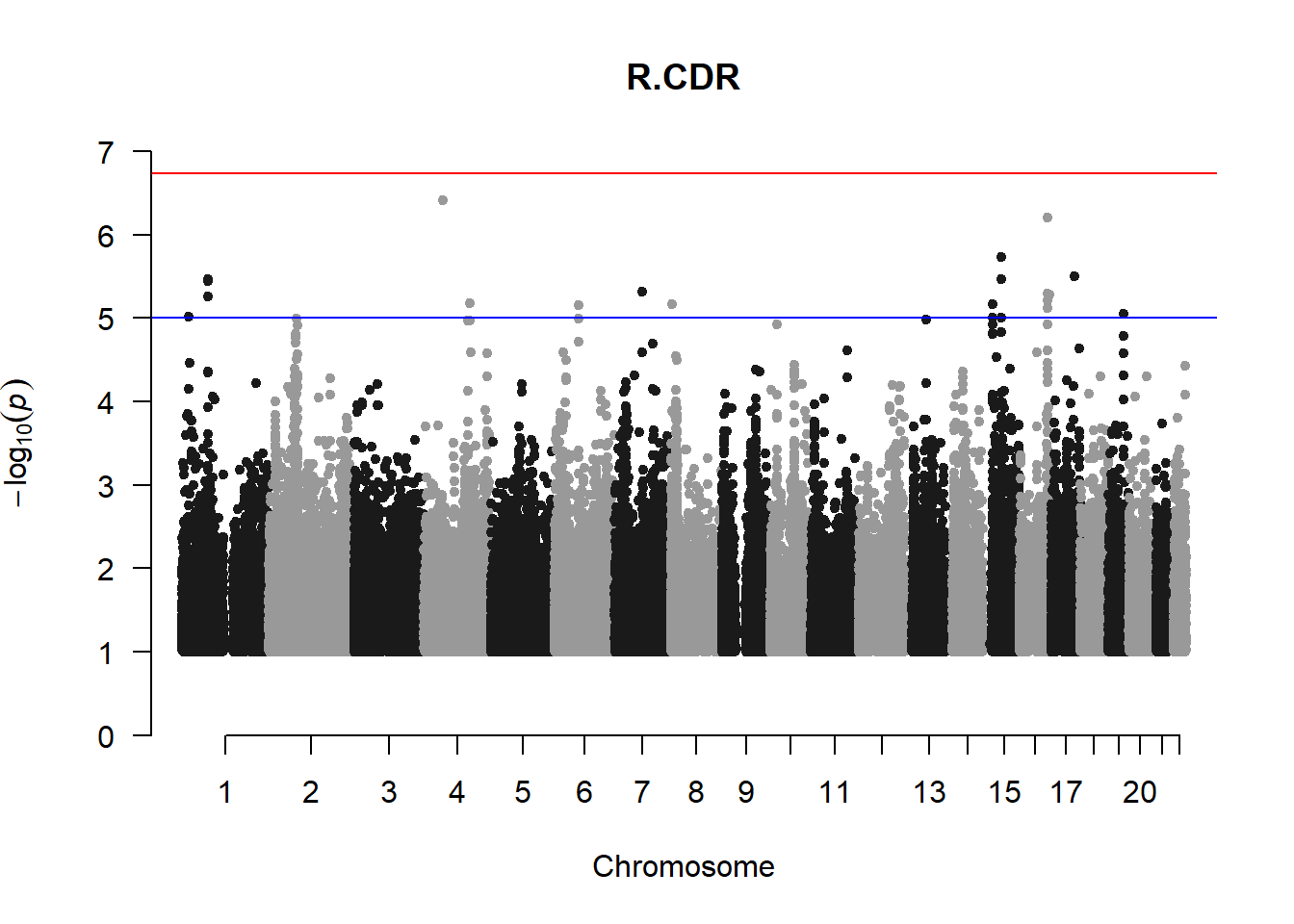
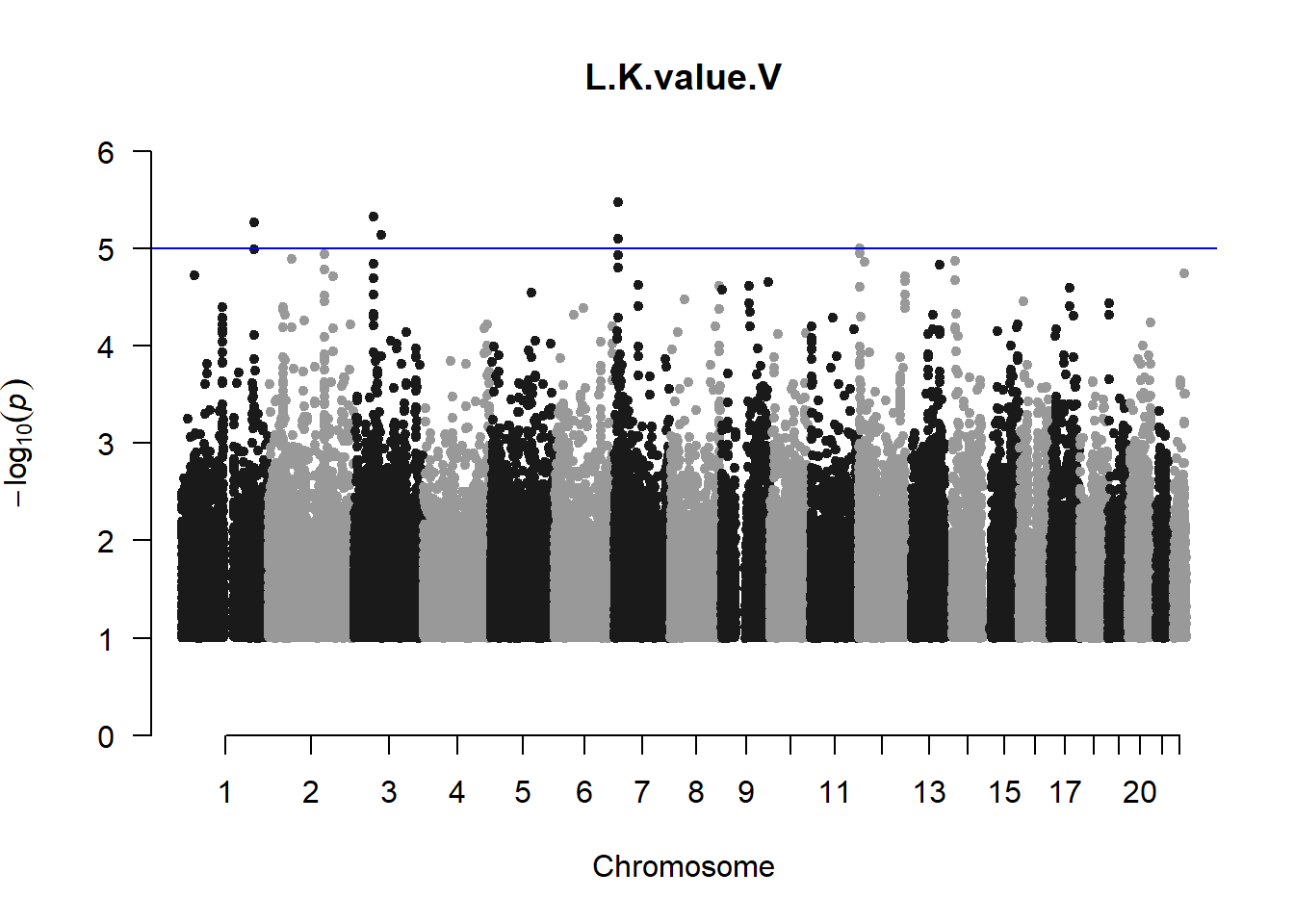
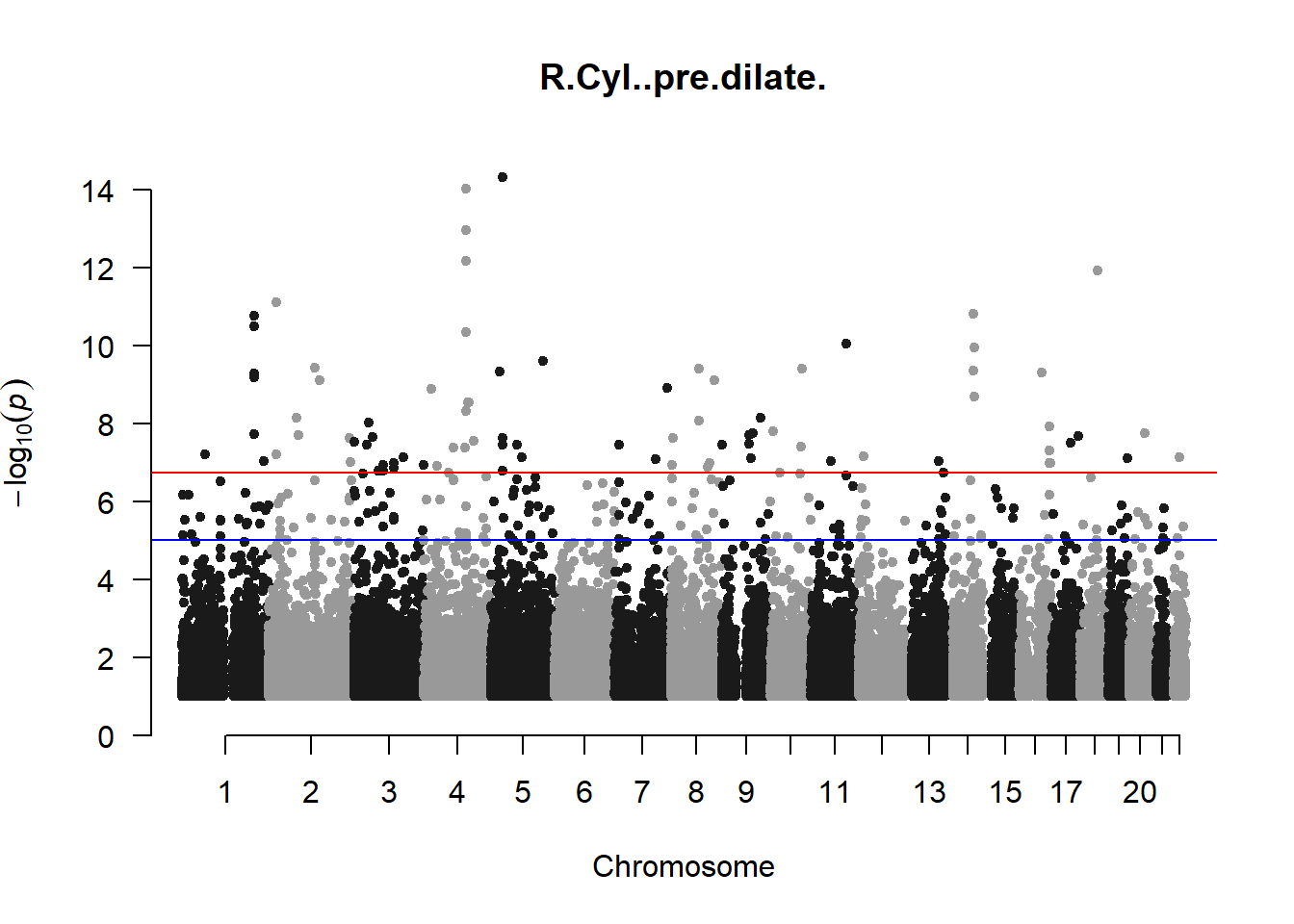
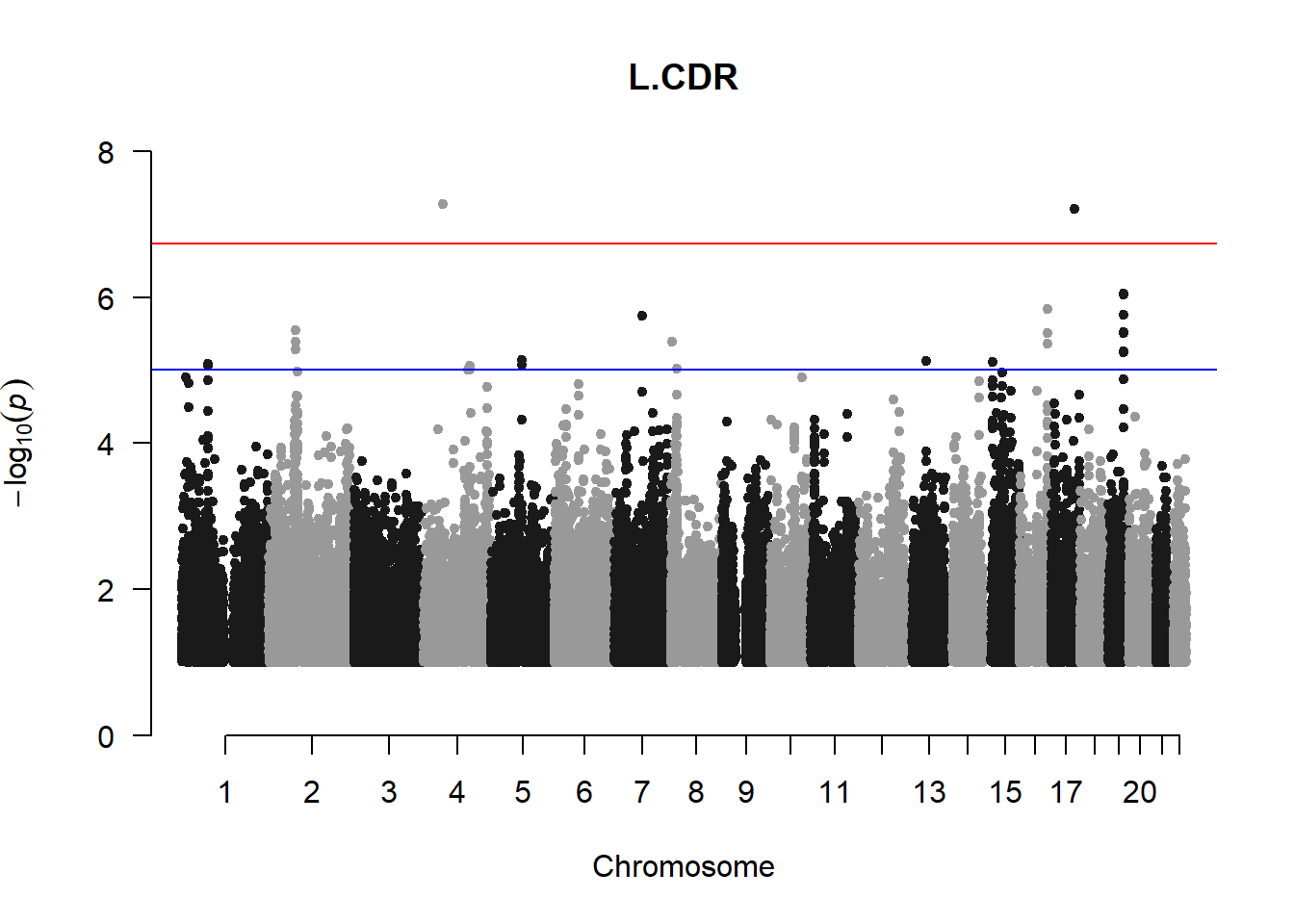
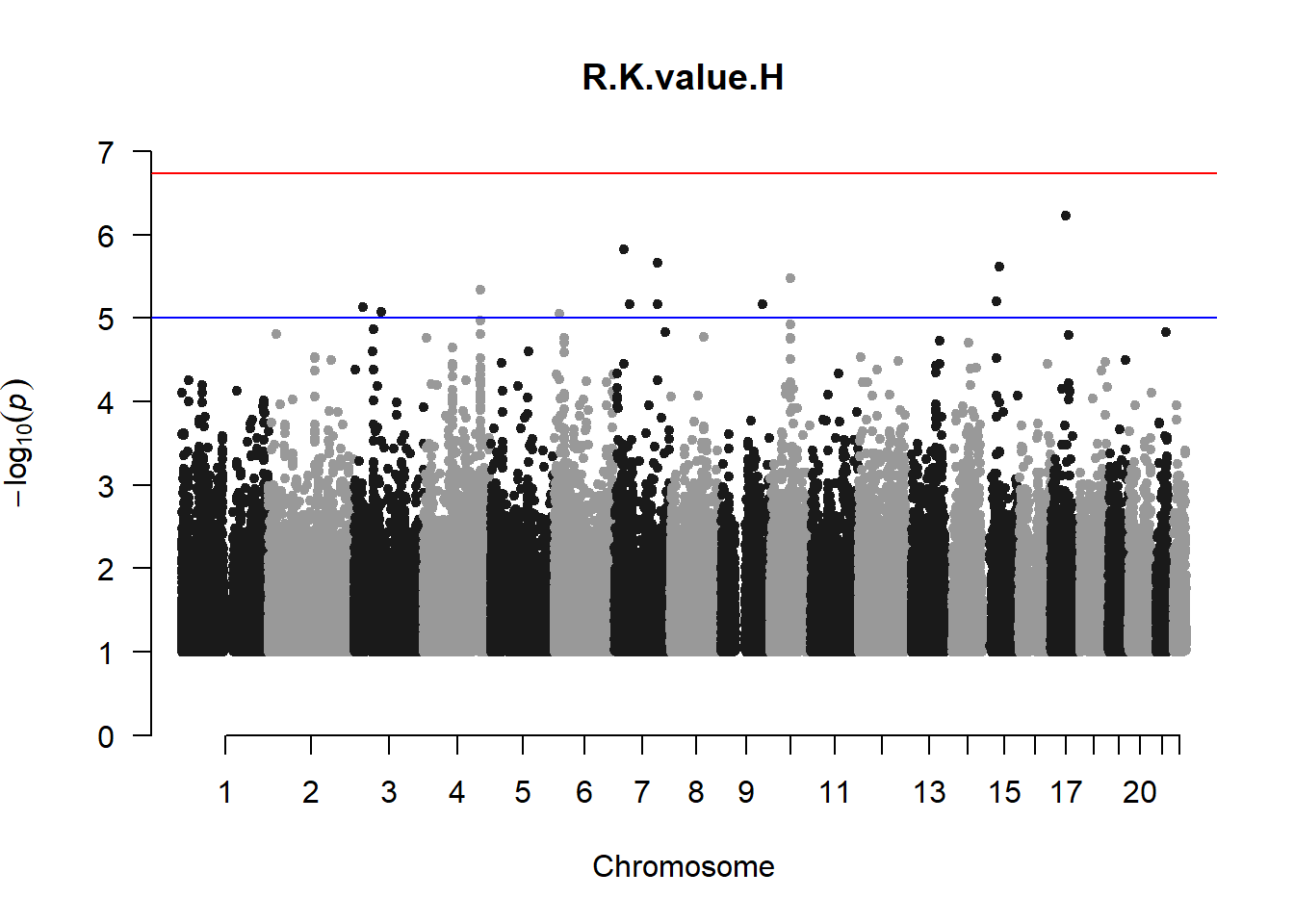
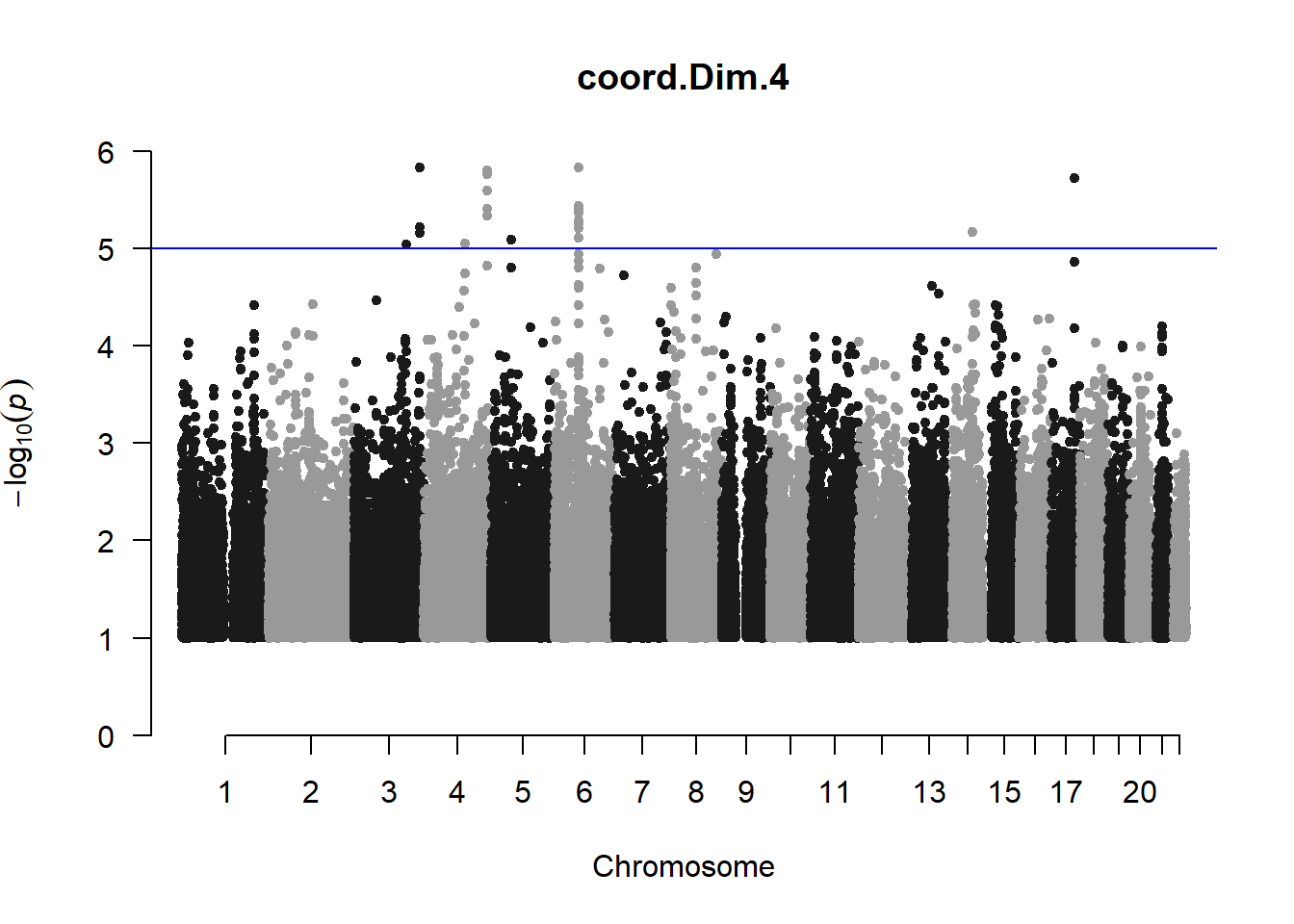
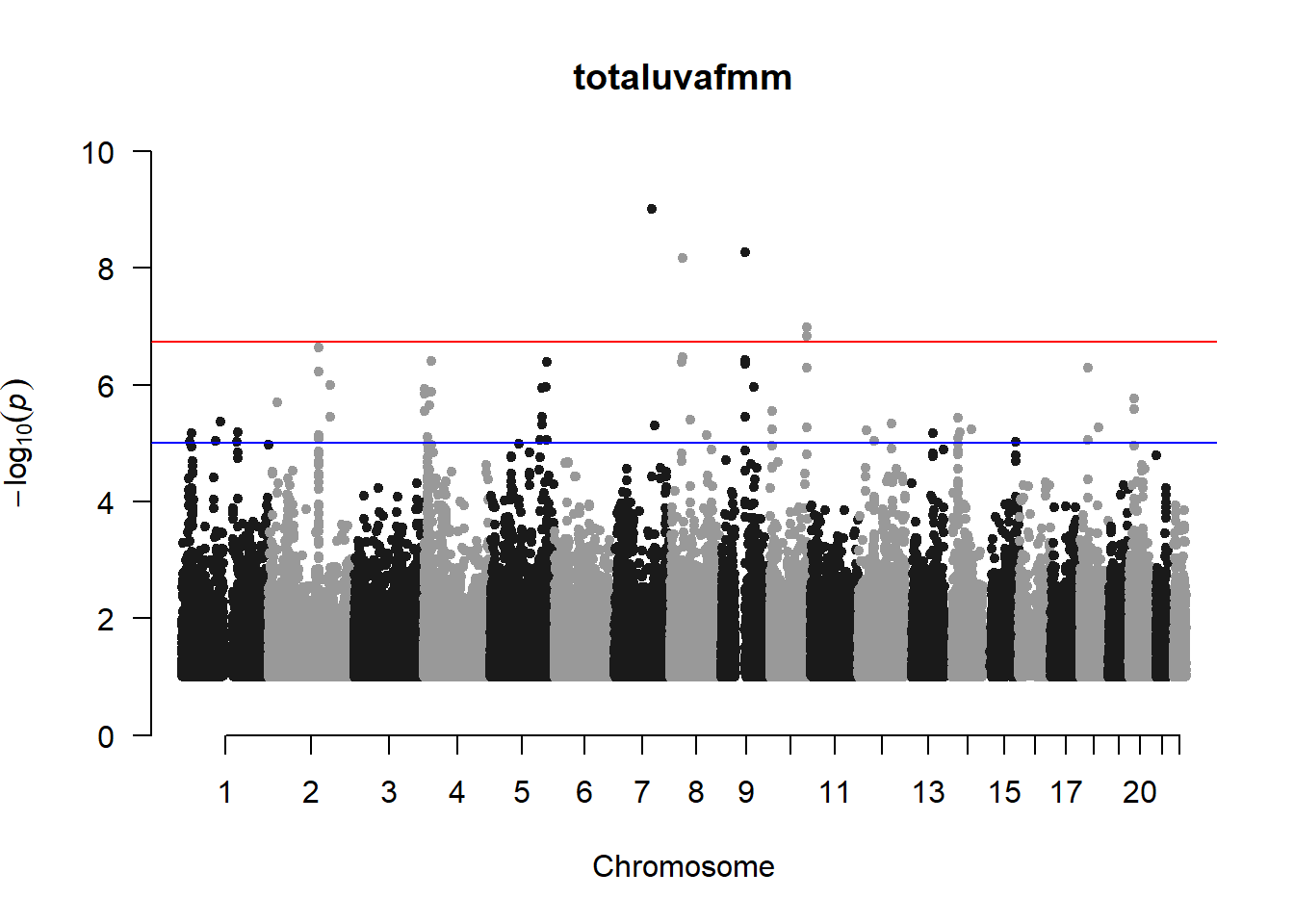
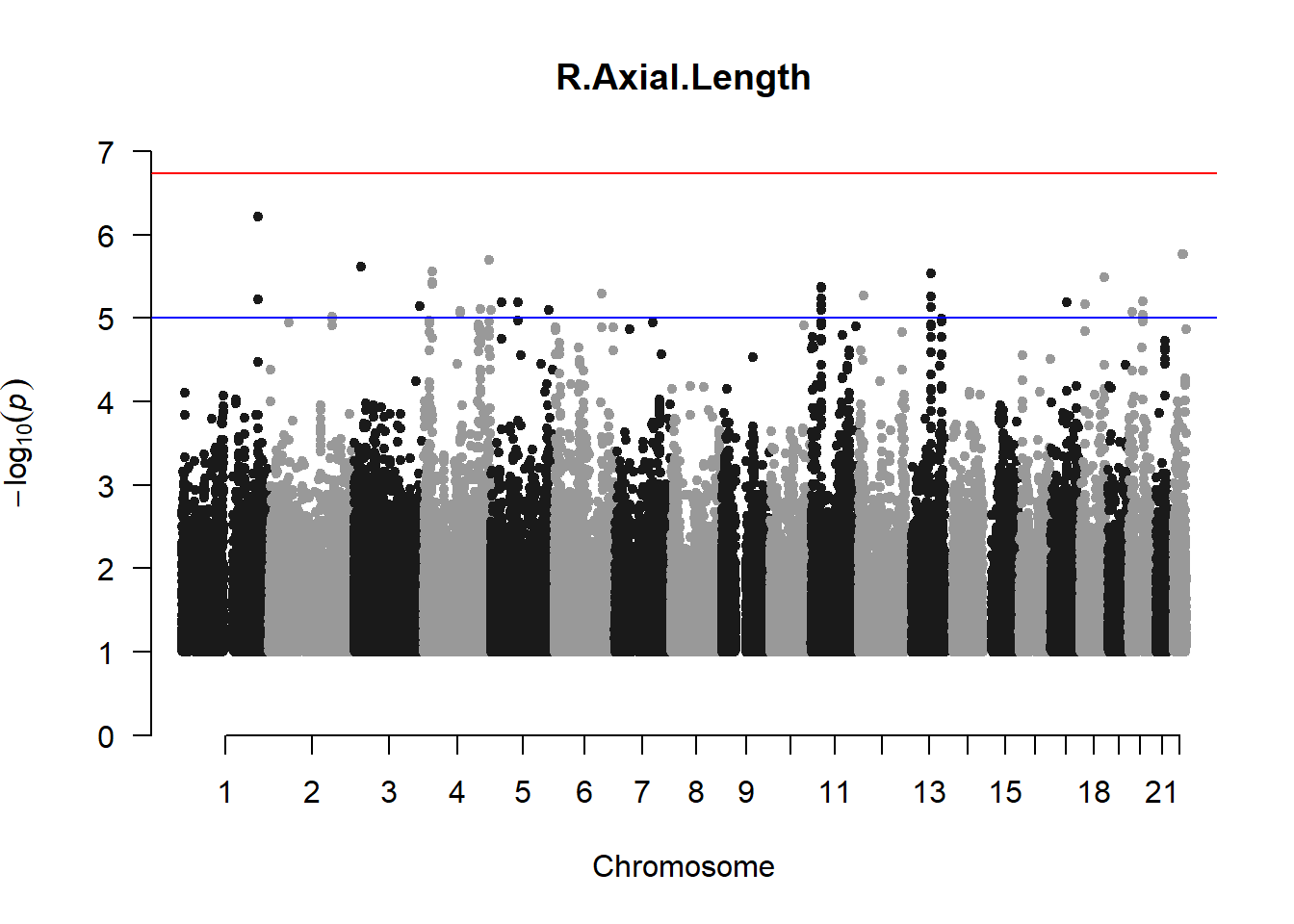
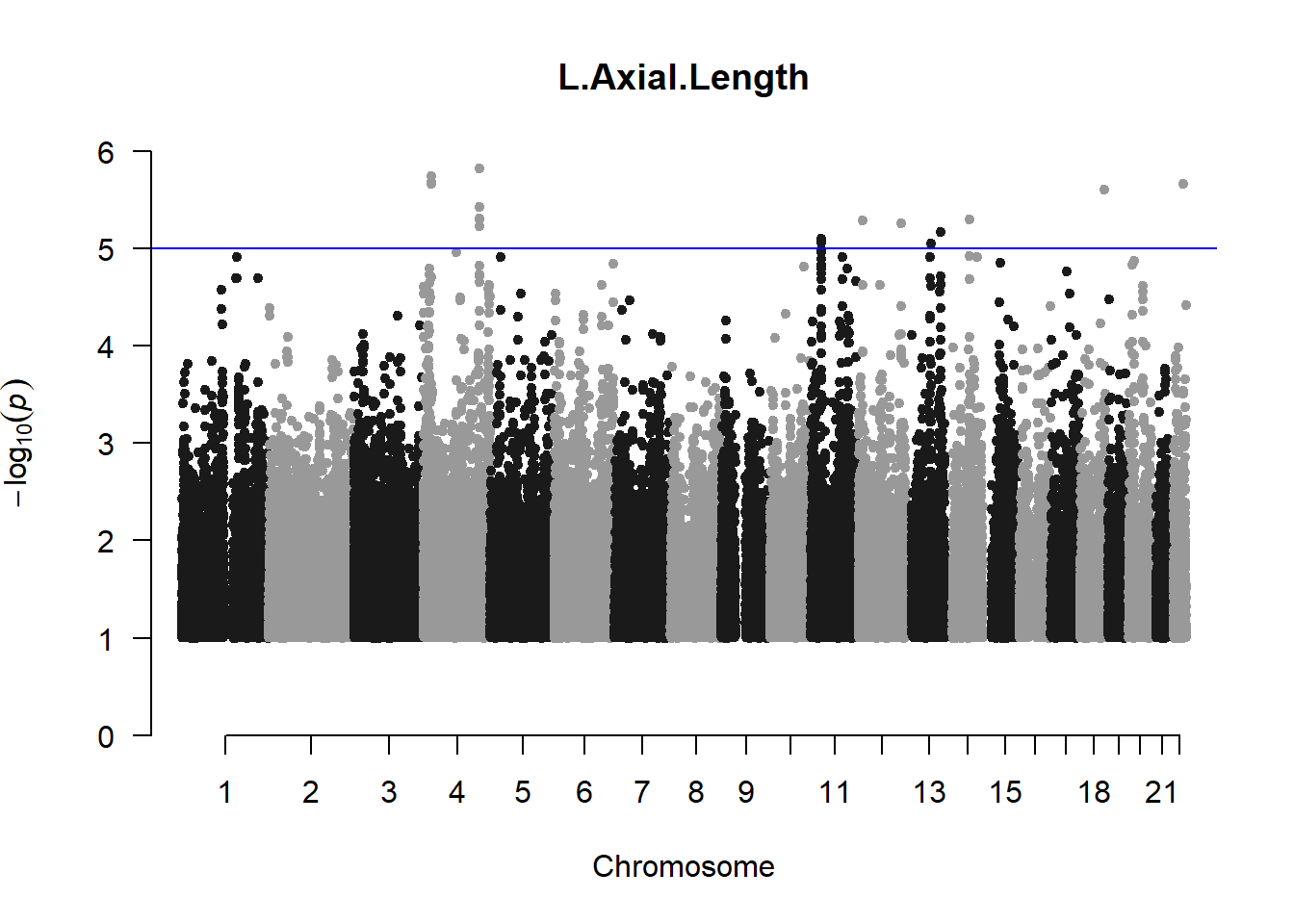
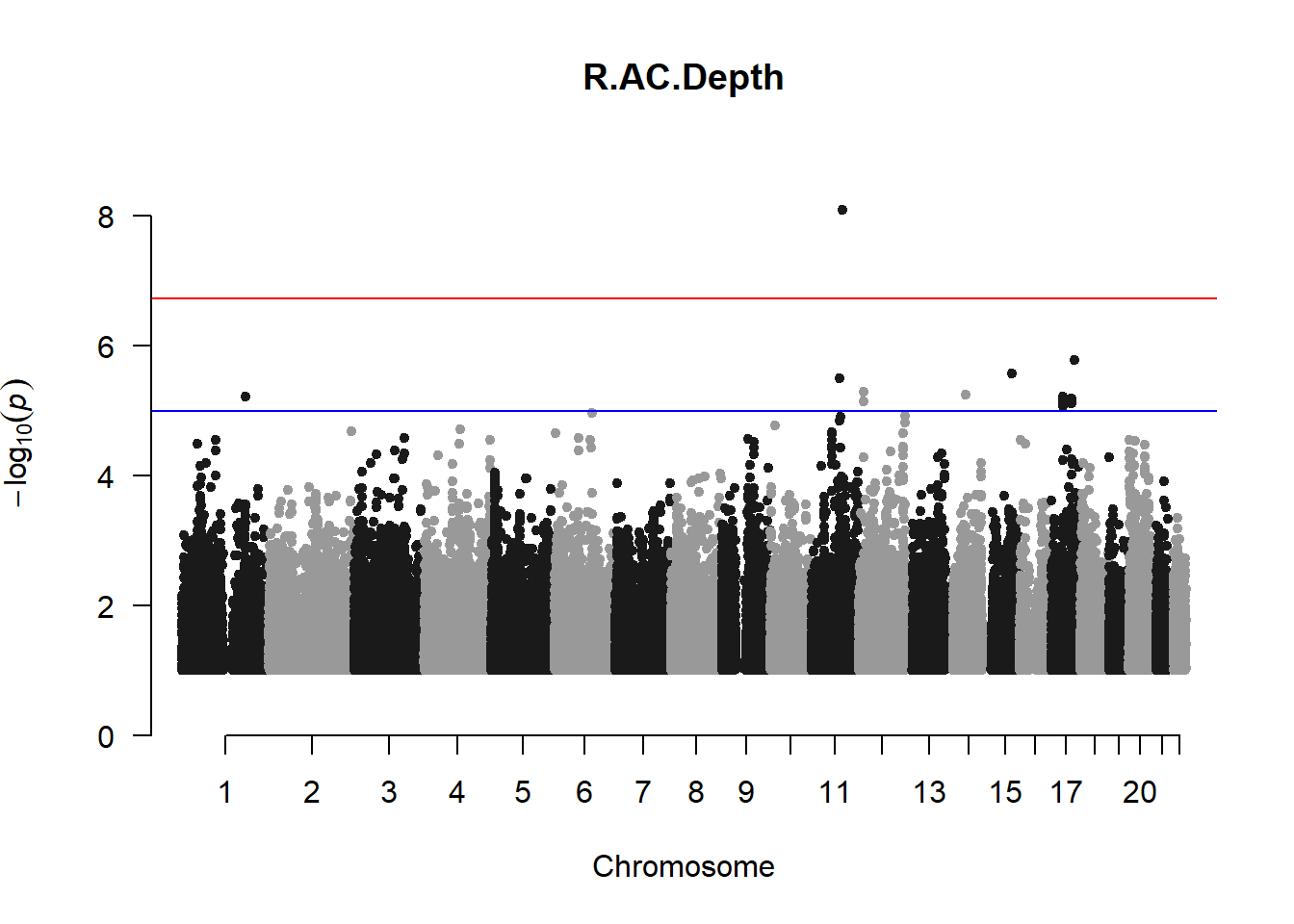
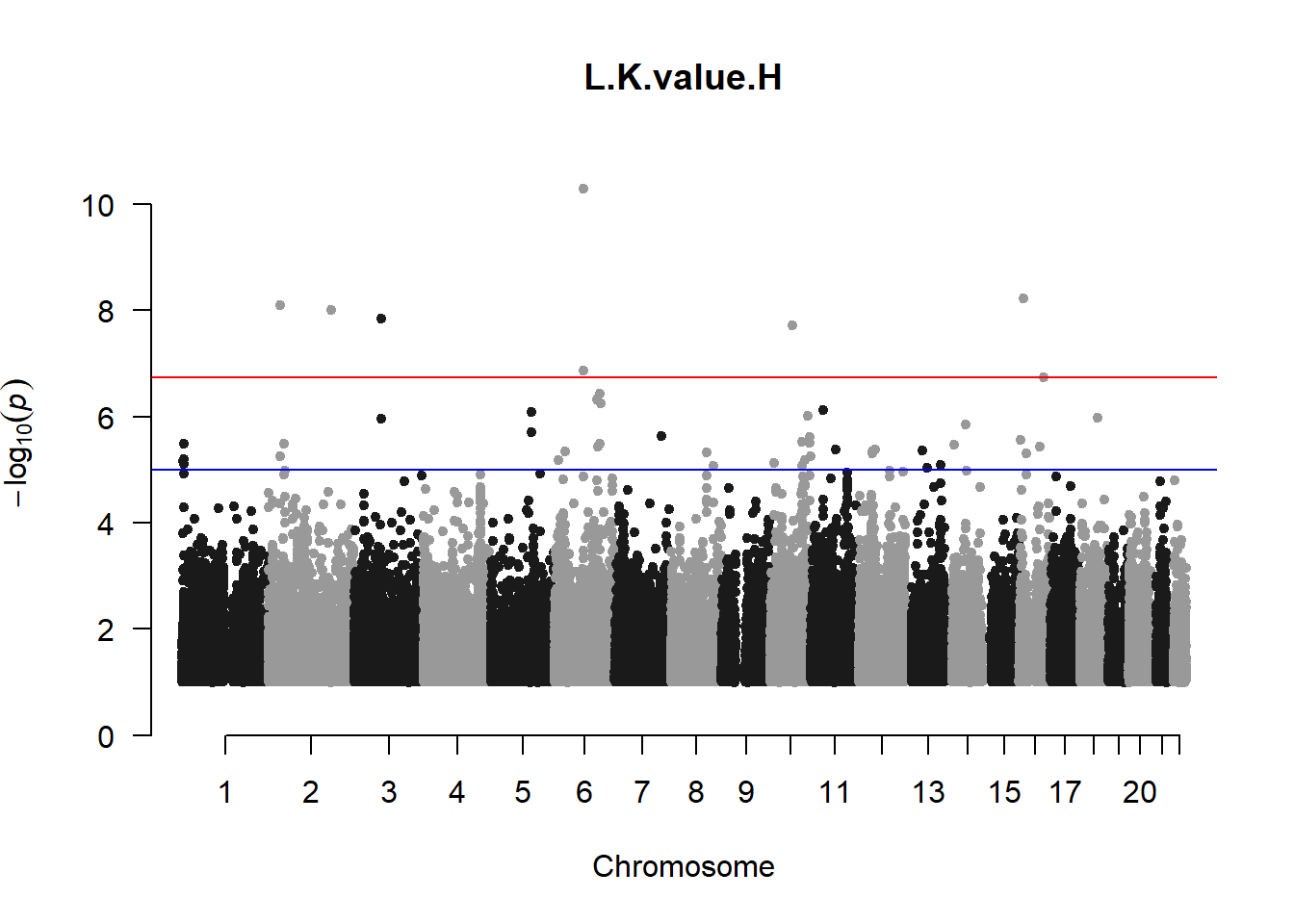
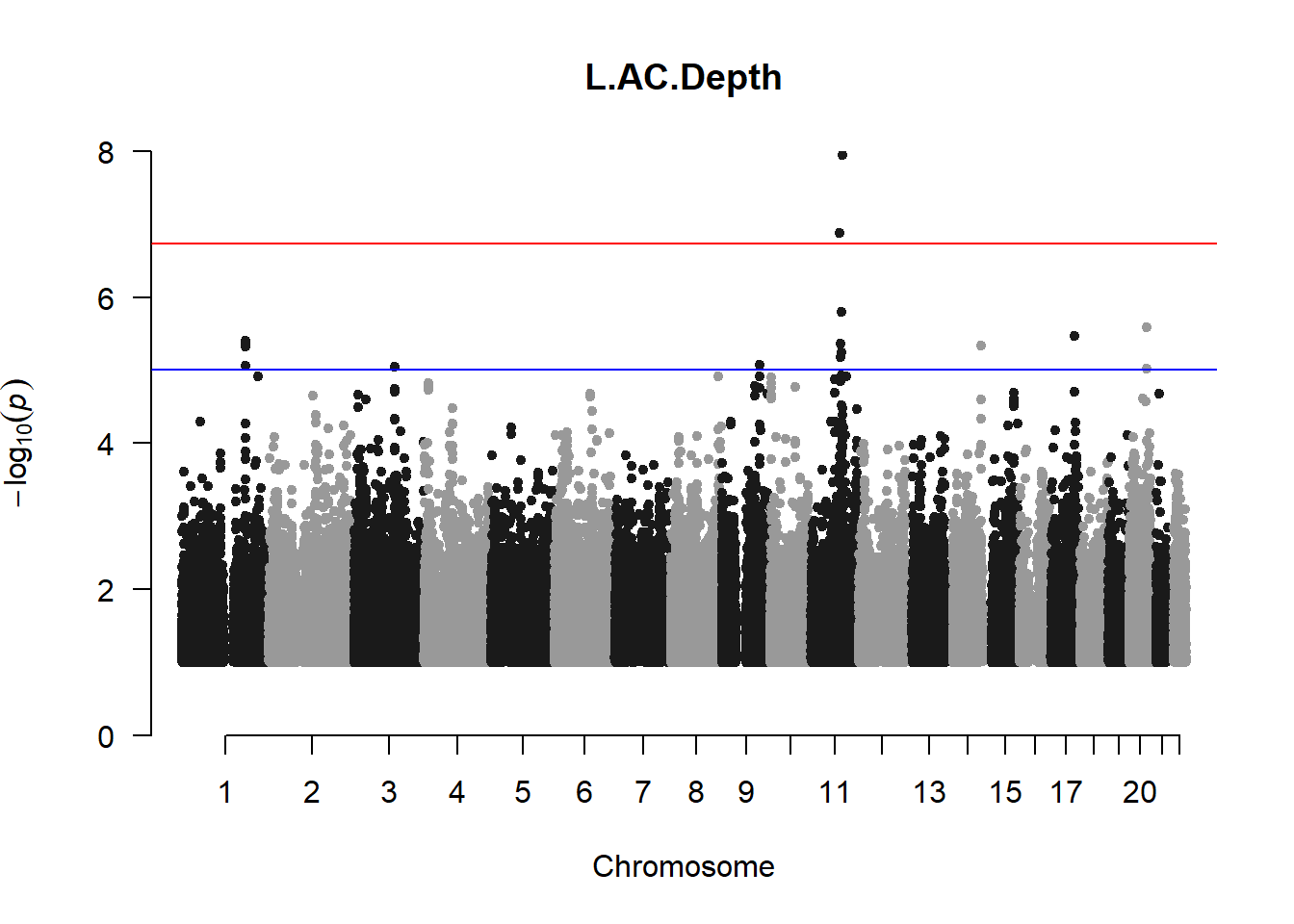
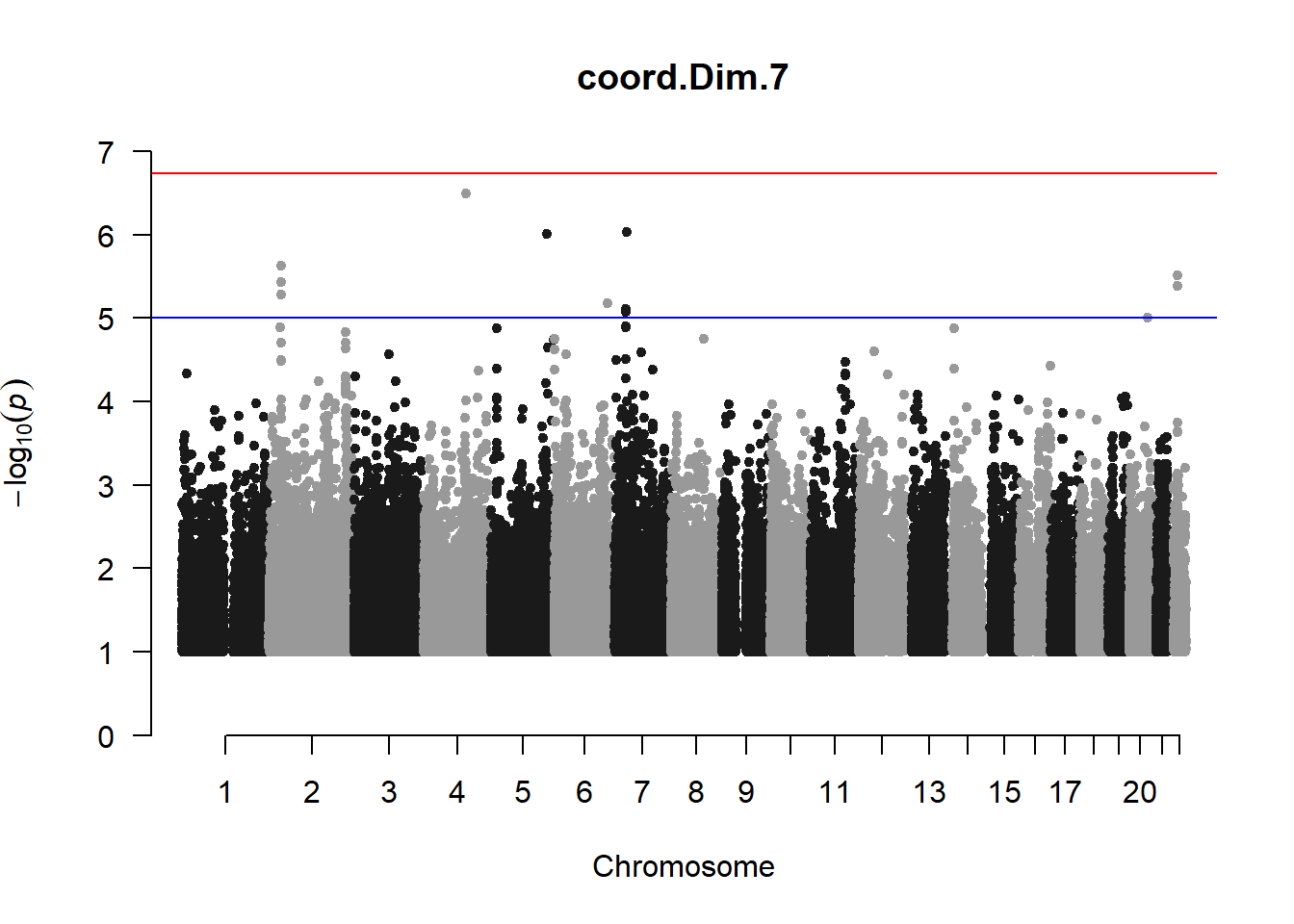
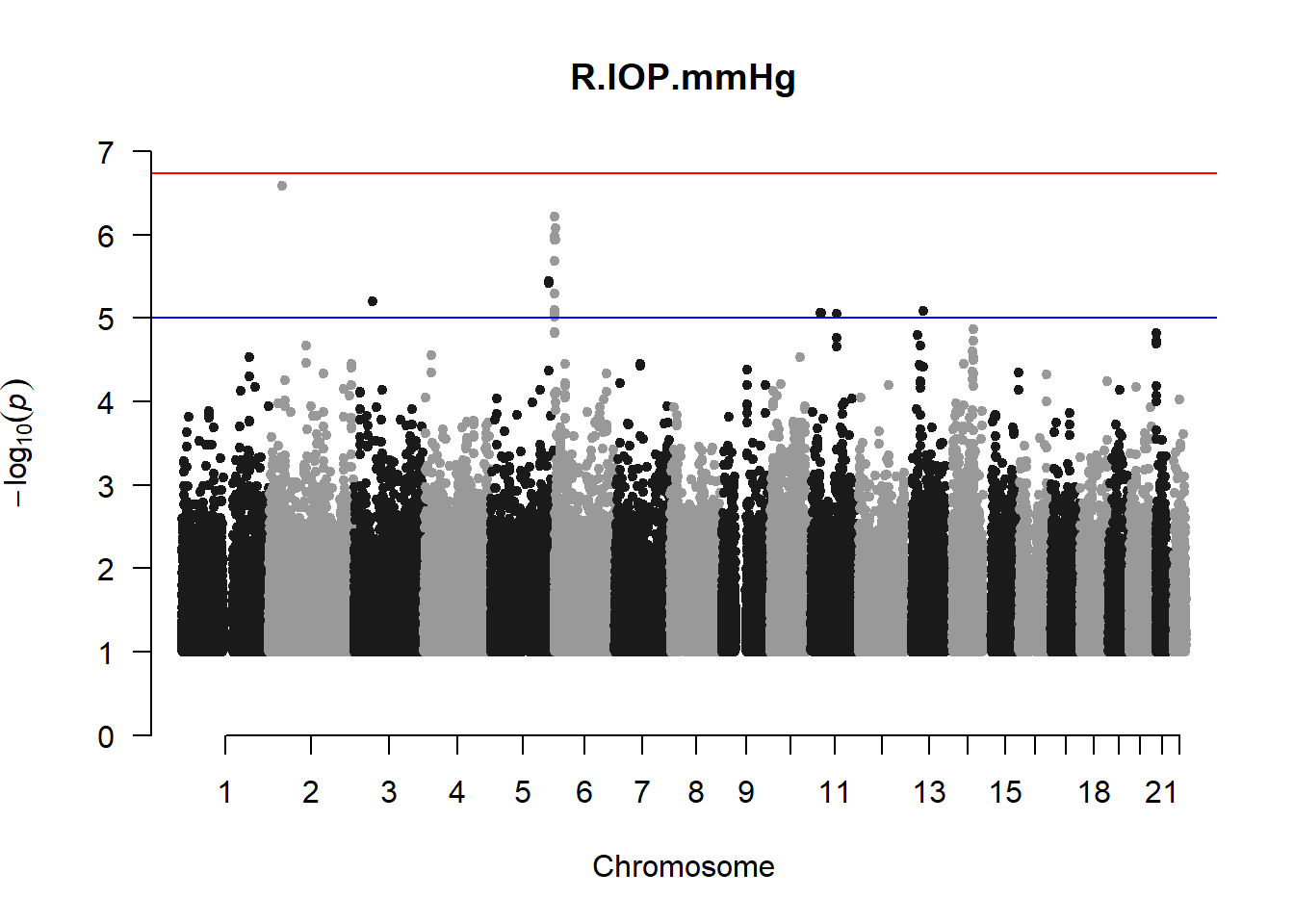
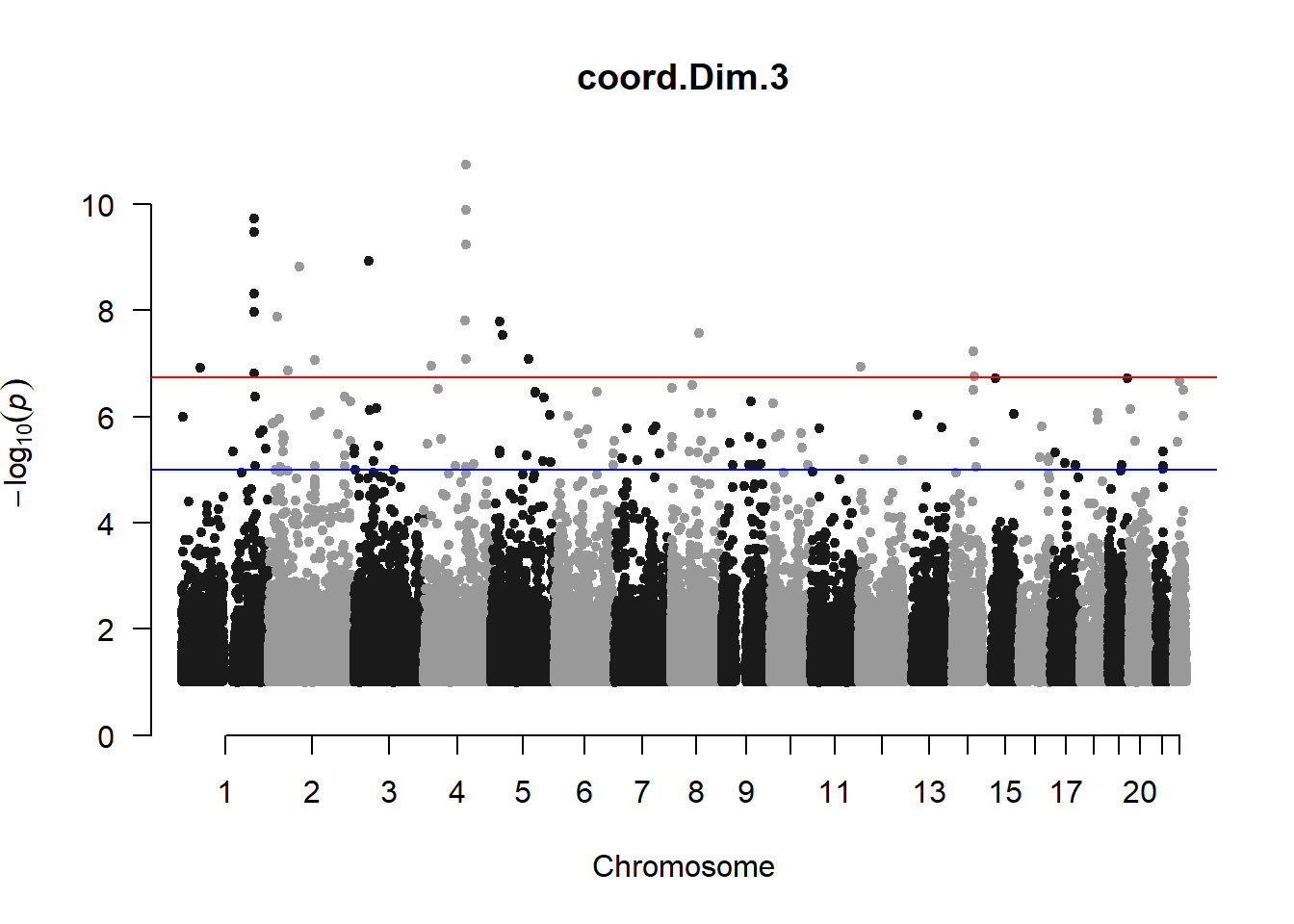
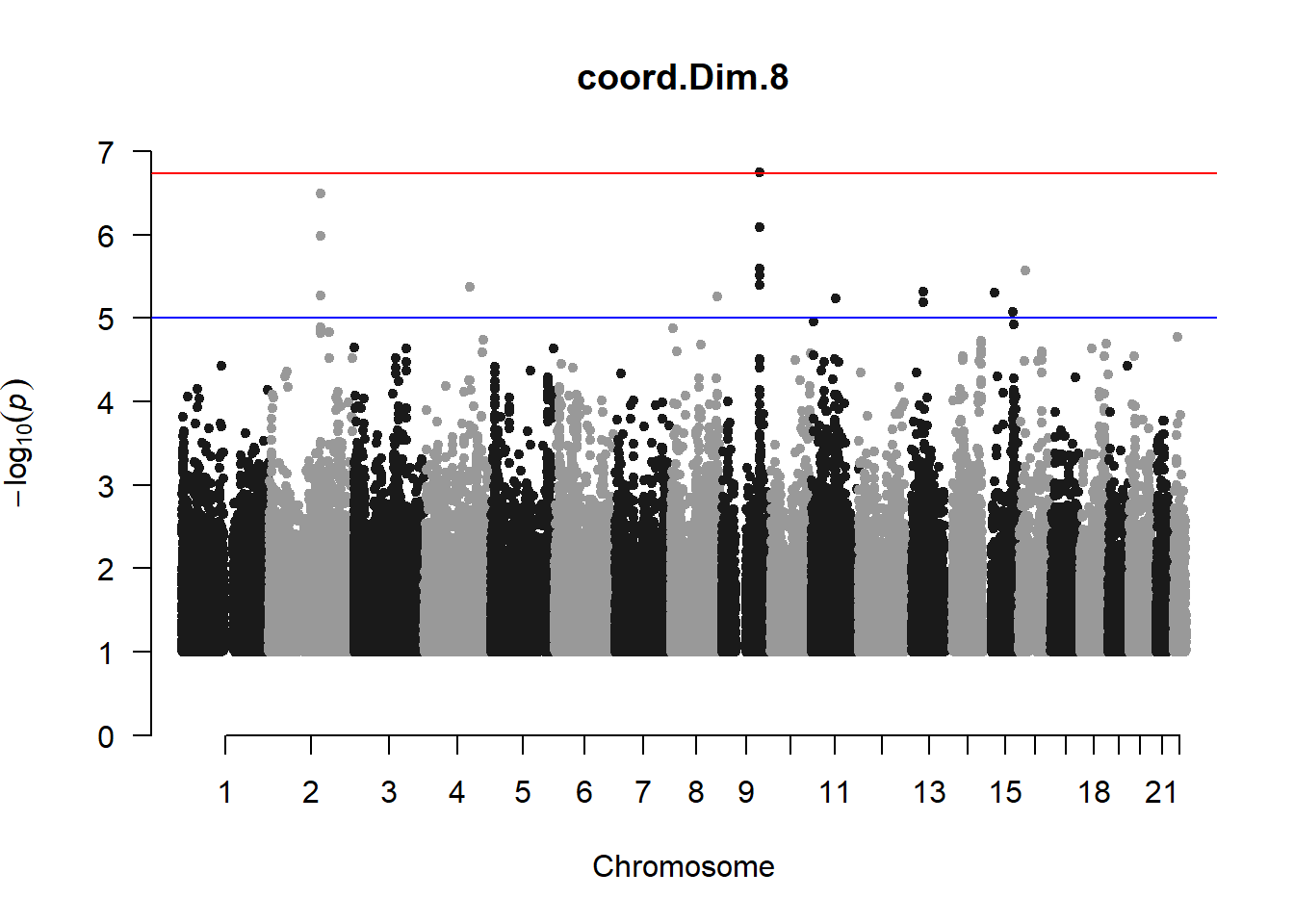
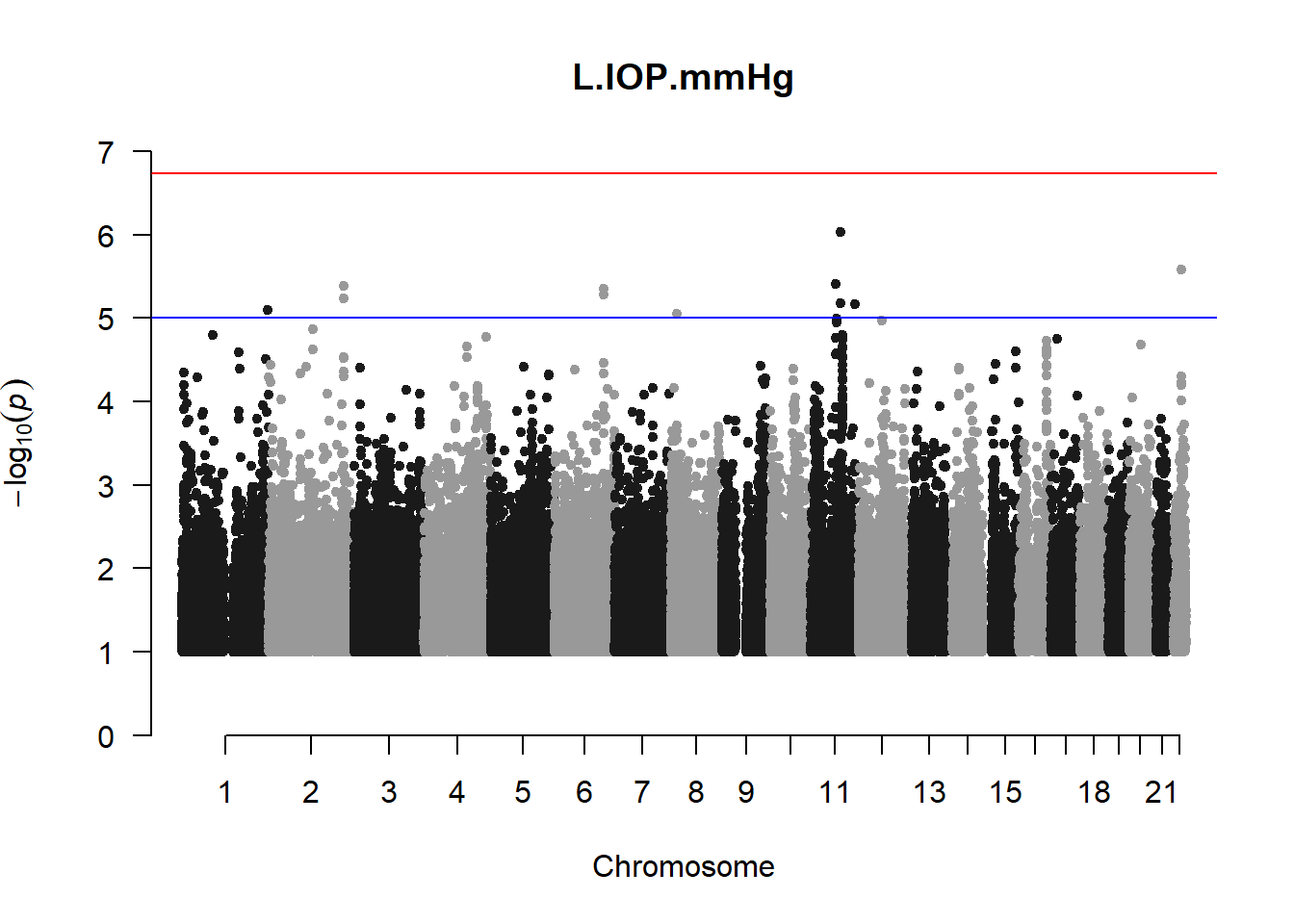
The loop above generates manhattan plots for the GWAS results of all 21 heritable traits.
6. Annotate manhattan plots with significant hits
I tried adding an annotation argument to the loop above to annotate hits that passed the genome-wide significance threshold. However, since not all manhattan plots had significant hits, the argument caused an error. I removed the argument from the loop and it was successful in generating all 21 manhattan plots. Of these, approximately 9 plots have significant hits and therefore require annotation.
###uvaf
uvaf_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$totaluvafmm, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
uvaf_gwas <- na.omit(uvaf_gwas)
uvaf_gwas_filtered <- uvaf_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = uvaf_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Ultraviolet Autofluorescence", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)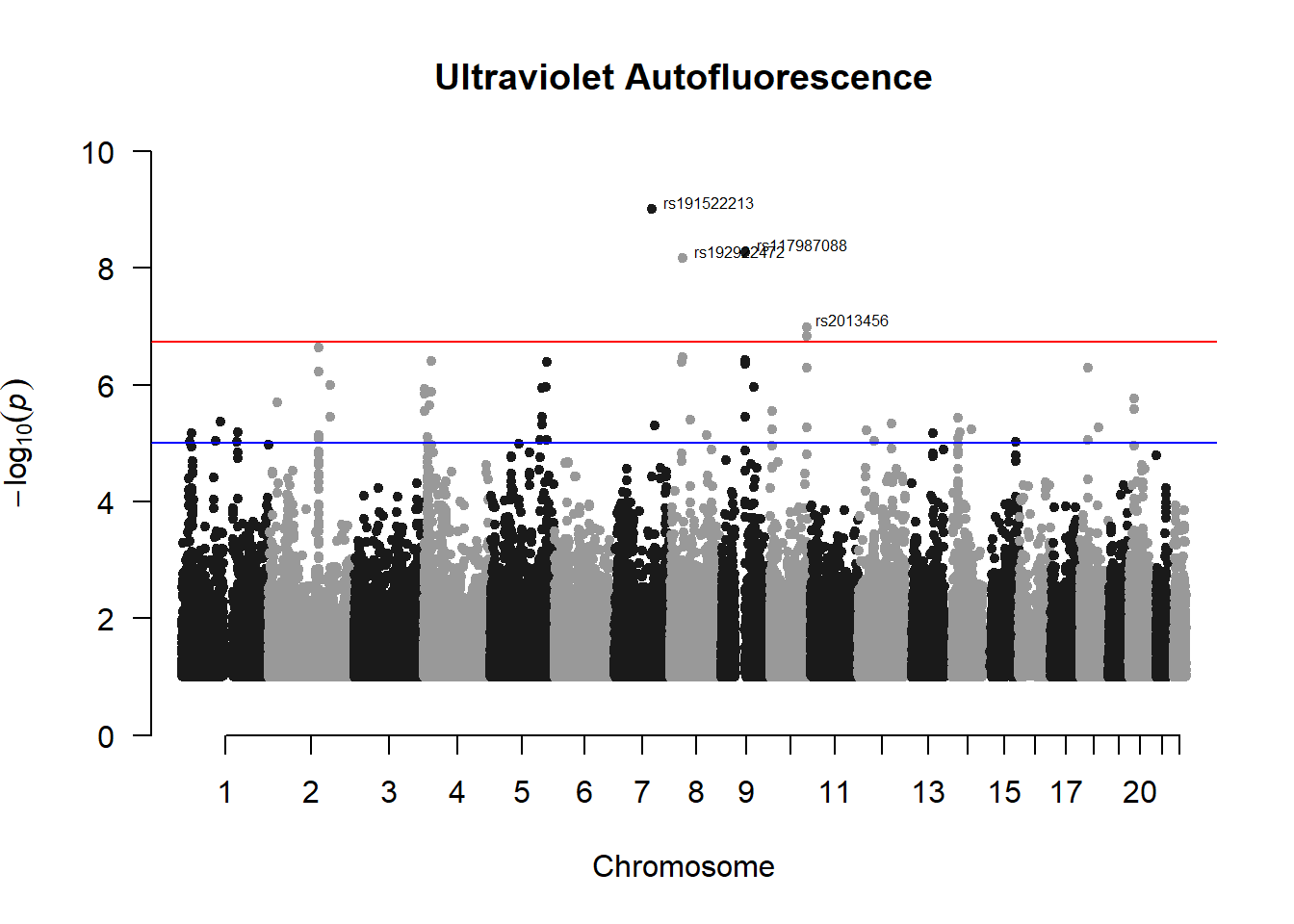
###PC3
pc3_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$coord.Dim.3, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
pc3_gwas <- na.omit(pc3_gwas)
pc3_gwas_filtered <- pc3_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = pc3_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Component 3", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)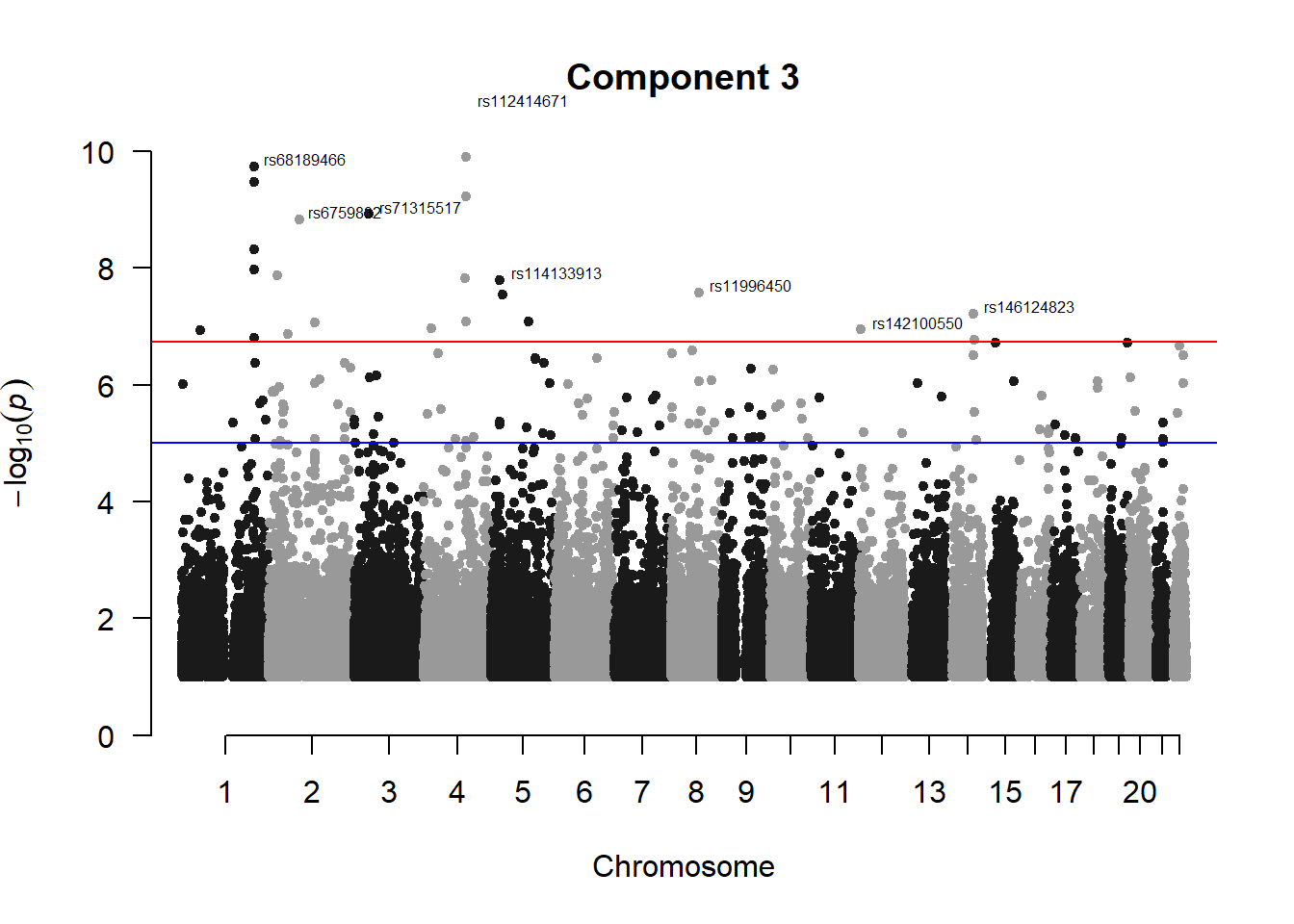
###PC8
pc8_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$coord.Dim.8, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
pc8_gwas <- na.omit(pc8_gwas)
pc8_gwas_filtered <- pc8_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = pc8_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Component 8", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)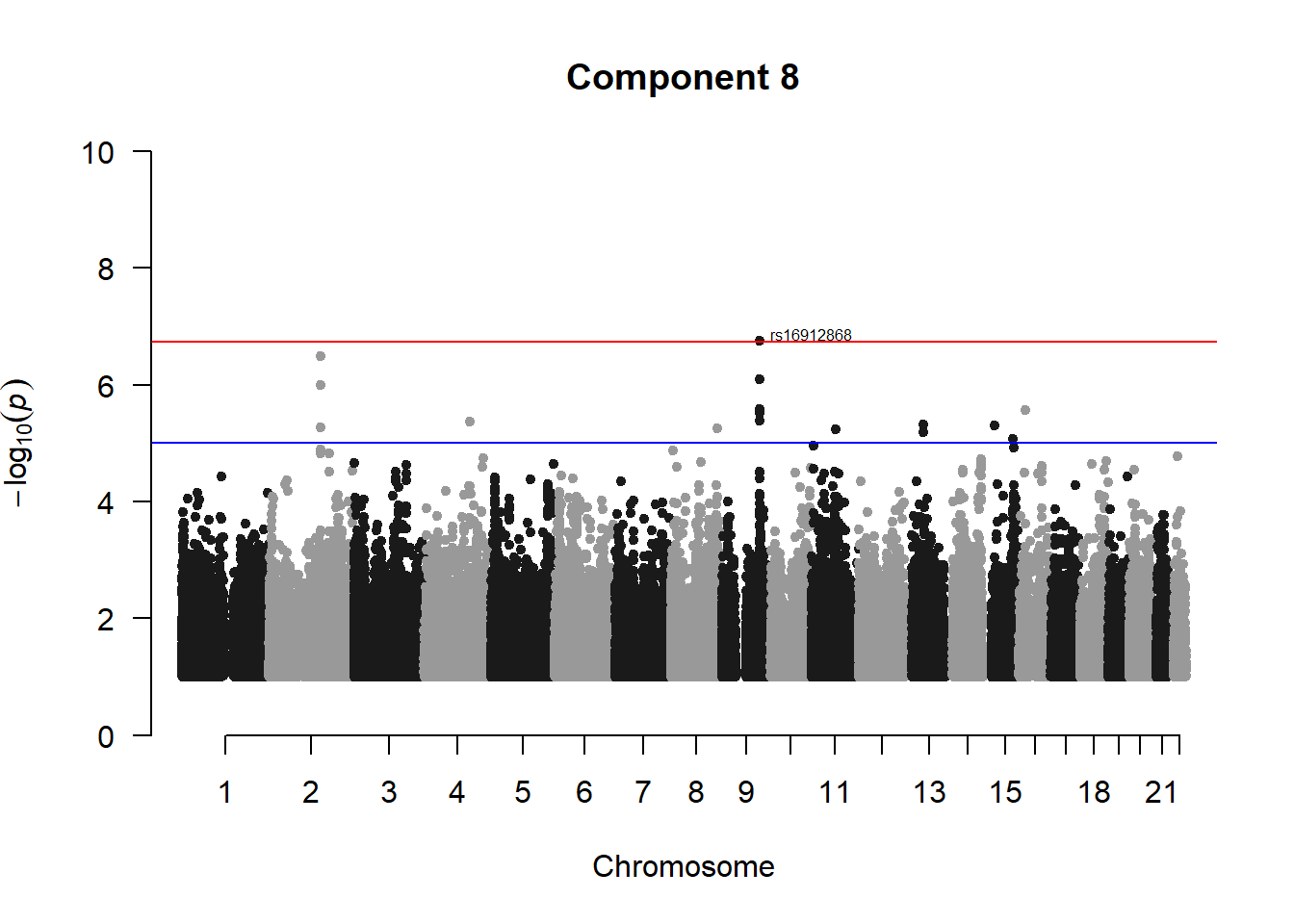
###L ACD
l_acd_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$L.AC.Depth, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
l_acd_gwas <- na.omit(l_acd_gwas)
l_acd_gwas_filtered <- l_acd_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = l_acd_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Left Anterior Chamber Depth", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)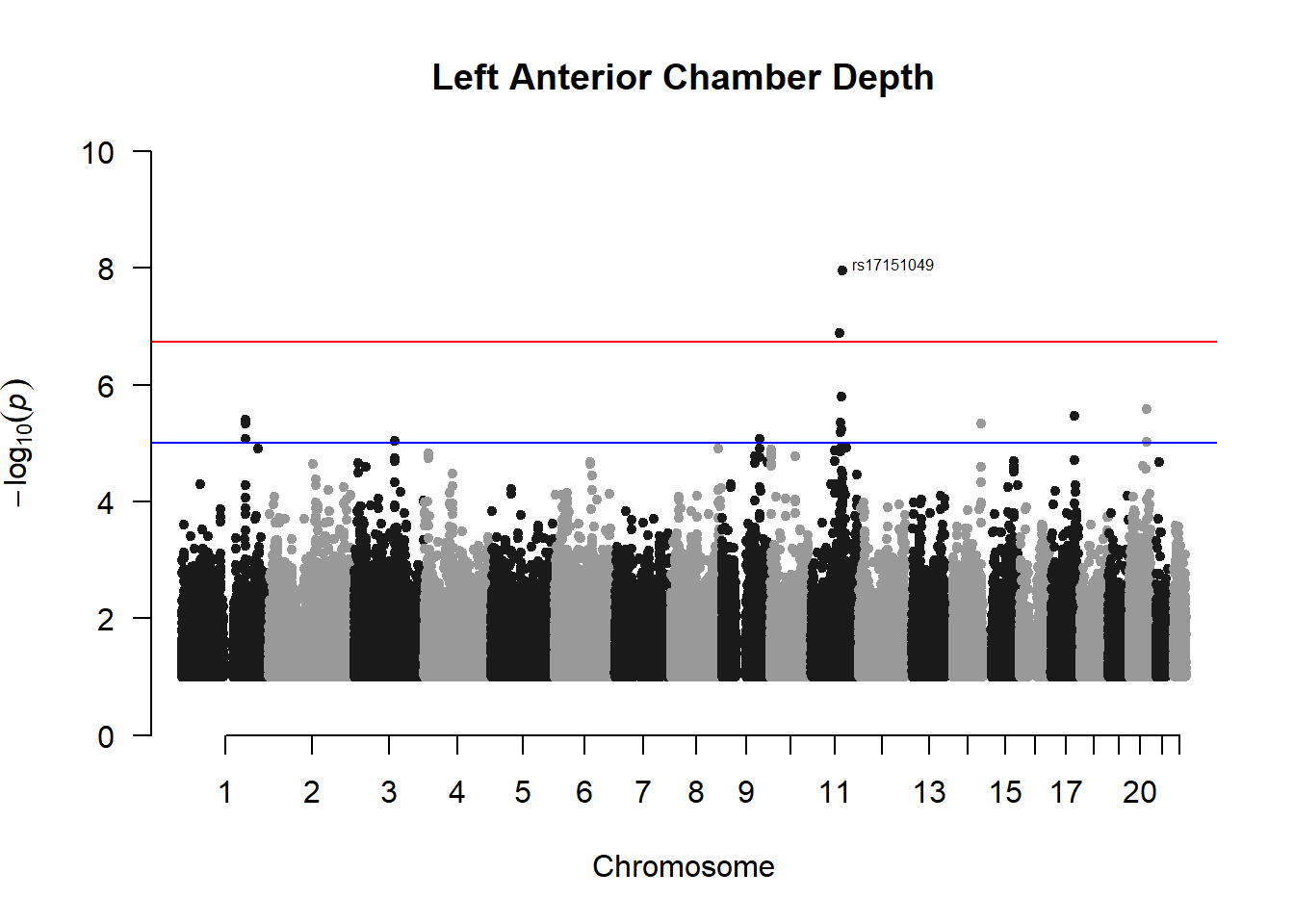
###L CDR
l_cdr_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$L.CDR, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
l_cdr_gwas <- na.omit(l_cdr_gwas)
l_cdr_gwas_filtered <- l_cdr_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = l_cdr_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Left Cup-to-Disc Ratio", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)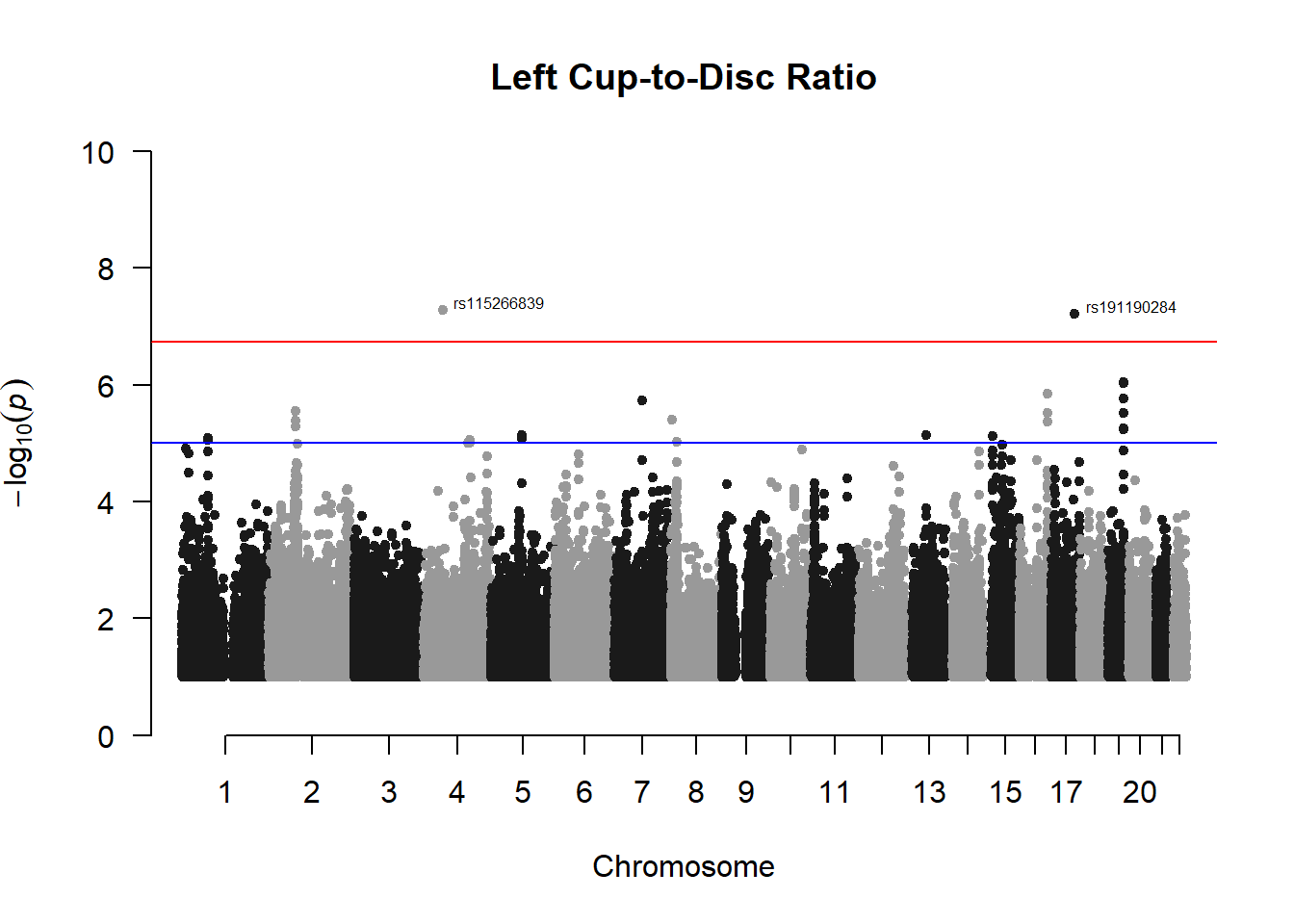
###L Kval H
l_KvalH_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$L.K.value.H, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
l_KvalH_gwas <- na.omit(l_KvalH_gwas)
l_KvalH_gwas_filtered <- l_KvalH_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = l_KvalH_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Left Horizontal K-value", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)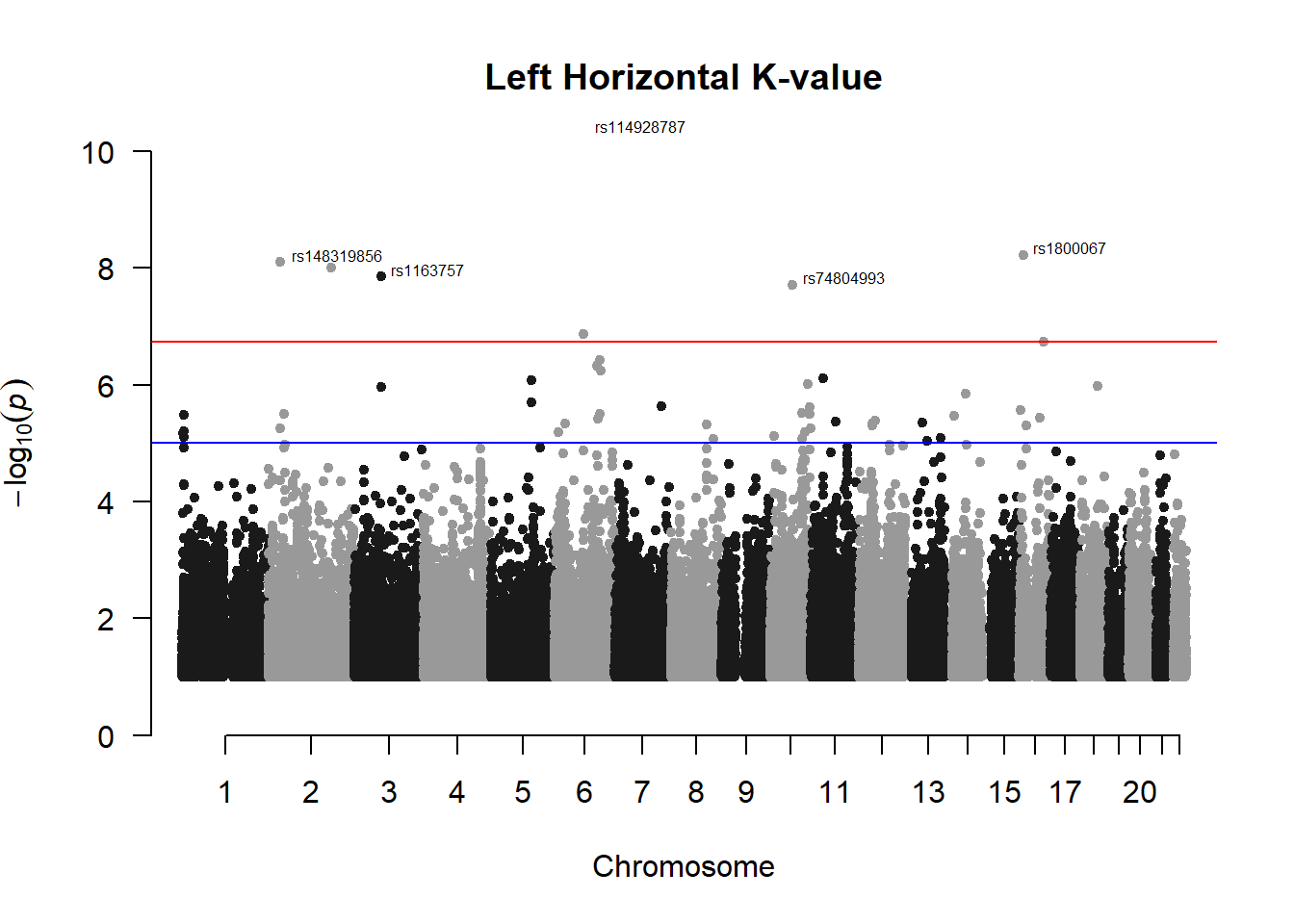
###R ACD
r_acd_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$R.AC.Depth, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
r_acd_gwas <- na.omit(r_acd_gwas)
r_acd_gwas_filtered <- r_acd_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = r_acd_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,10), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Right Anterior Chamber Depth", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)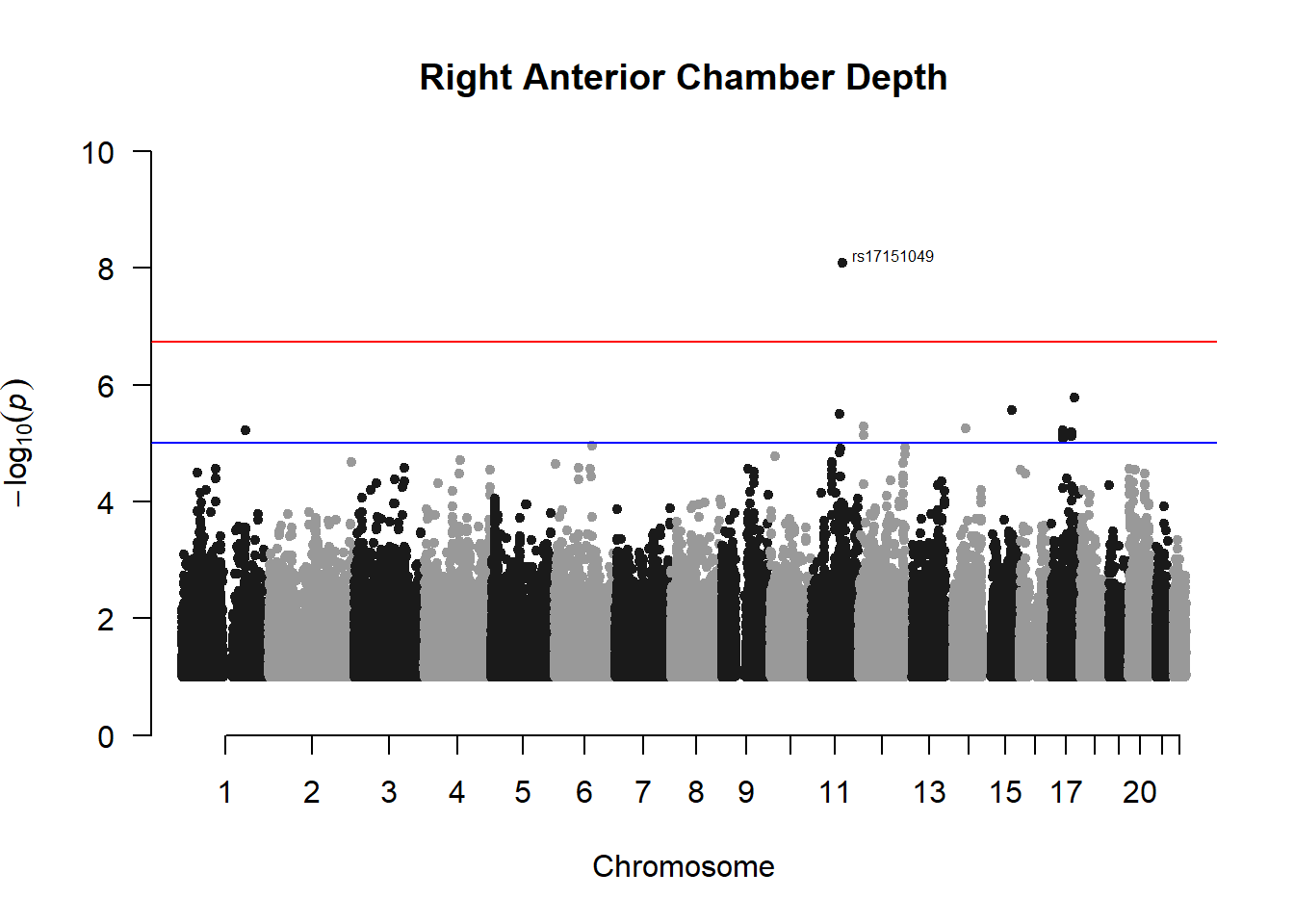
###R Cyl
r_cyl_gwas <- association.test(merged_nies_210818, nies_heritable_pheno$R.Cyl..pre.dilate, method="lmm", test = "lrt", K = merged_nies_GRM, eigenK = merged_nies_eiK, p = 2)
r_cyl_gwas <- na.omit(r_cyl_gwas)
r_cyl_gwas_filtered <- r_cyl_gwas %>% filter(-log10(p)>1) %>% filter(freqA2 < 0.99)
manhattan(x = r_cyl_gwas_filtered, chr = "chr", bp = "pos", p = "p", snp = "id", ylim = c(0,15), genomewideline = -log10(1.84e-7), main = "Right Cylindrical Pre-Dilate Refractive Error", annotatePval = 1.84e-7)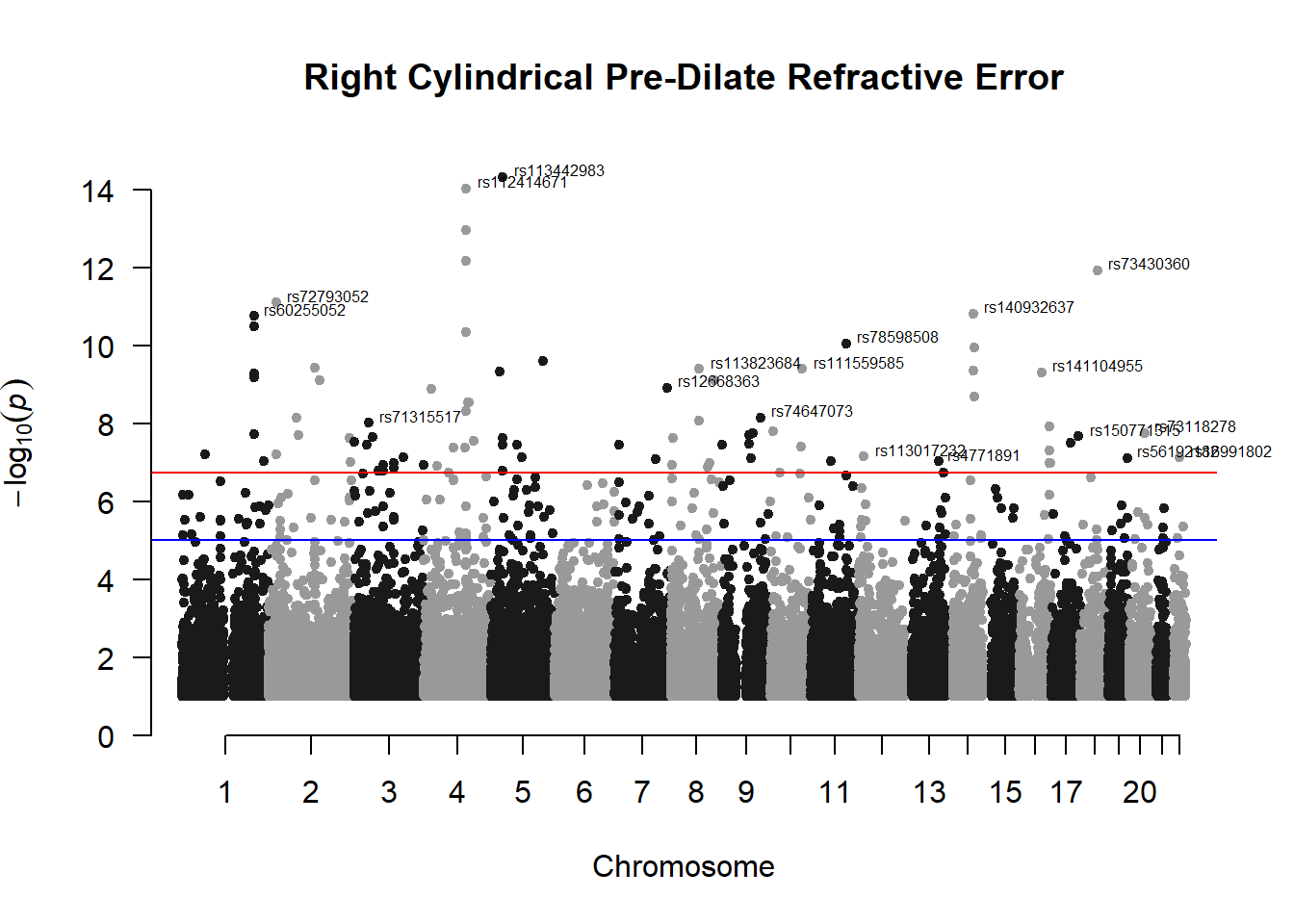
These manhattan plots display significant SNPs that pass the genome-wide significance threshold. Although this indicates significant association with traits, they may not all be “true”. Typically, robust associations, or significant results have supporting SNPs surrounding the most significant peak. Therefore, I will apply a filter on these results.