| tags: [ Genomic Data Linux PCA PLINK R ] categories: [Coding Experiments ]
Performing PCA on genomic data
Introduction
The final step to the second part of aim 1 is to perform a PCA on the genomic data to investigate the population structure. This is important because it will allow me to determine if there are any underlying genetic structures in the genomic data and I can account for relatedness among individuals for subsequent analyses.
Methods and Results
1. Run PCA
plink1.9 --bfile merged_nies --pca 180 var-wts --out plink_output/nies_final_pcaThe count had to be increased (default is 20) because there are over 100 components with an eigenvalue >1.
Including the var-wts modifier will generate a file for variant weights.
2. Load eigenvalue results
nies_final_pca_eigenval <- read.table('C:/Users/Martha/Documents/Honours/Project/honours.project/Data/plink_output/nies_final_pca.eigenval', header = F)
head(nies_final_pca_eigenval)## V1
## 1 4.25322
## 2 3.95956
## 3 3.18262
## 4 2.86084
## 5 2.80460
## 6 2.732553. Produce screeplot
barplot(nies_final_pca_eigenval$V1,
names.arg = 1:nrow(nies_final_pca_eigenval),
main = "NIES PCA Eigenvalue",
xlab = "Principal Components",
ylab = "Eigenvalue",
col ="lightskyblue2")
lines(x = 1:nrow(nies_final_pca_eigenval), nies_final_pca_eigenval$V1,
type = "b", pch = 19, col = "red")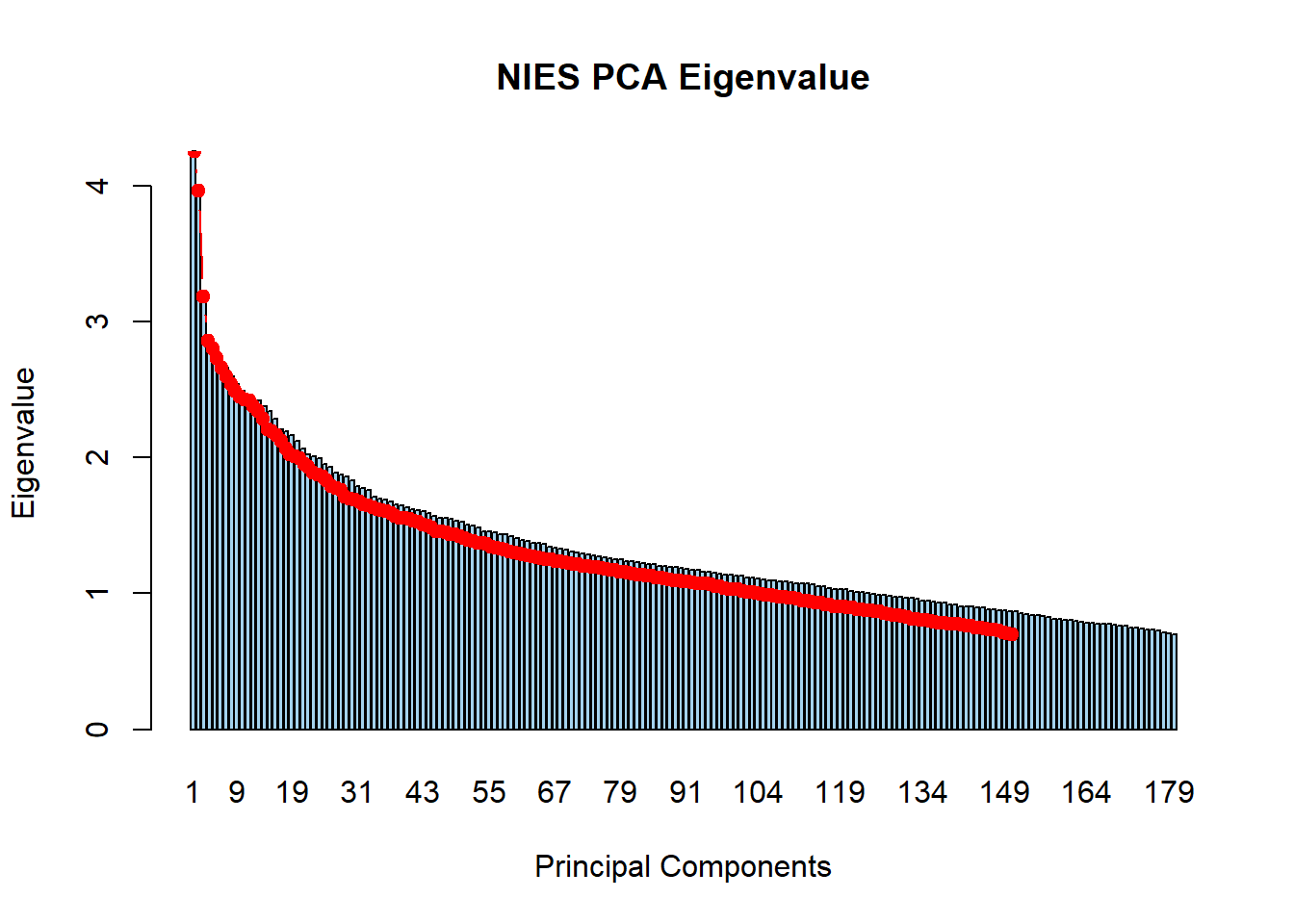
There are 124 principal components that have an eigenvalue >1.